Figure 5.
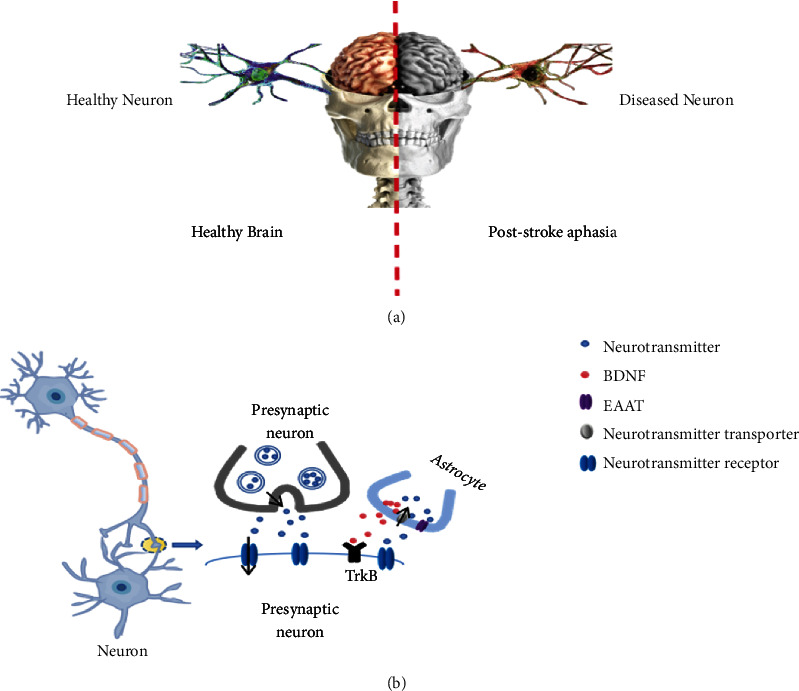
The neuronal changes after PSA. (a) Compared with the healthy brain, the regular neuronal activity in PSA patients was blocked and replaced by pathological neurons. (b) In the healthy brain, neurotransmitters signal between synapses; BDNF secreted by astrocytes binds to TrkB to participate in synaptic growth, and EAAT maintains extracellular glutamate homeostasis. Neurotransmitter conduction is blocked, and the availability of neurotransmitters on synapses is reduced after stroke. The balance of neurotransmitter activity is broken, impairing the integrity of the neural pathway. Thus, dysfunction occurs.
