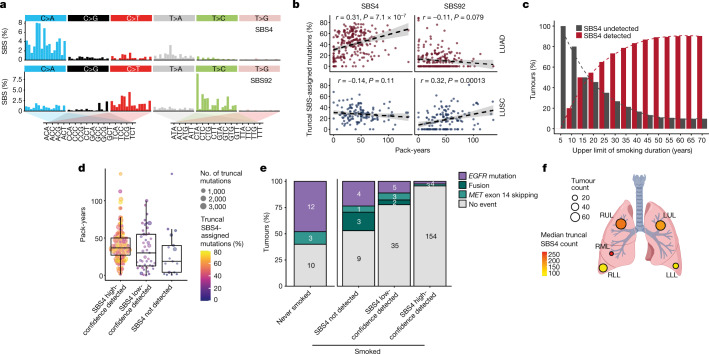
Fig. 2. Clinical and physiological determinants of SBS4-associated mutagenesis in NSCLC.
a, Signature profiles of SBS4 and SBS92 as reported using COSMIC (v.3.2). b, The correlation between smoking-mediated mutations (SBS4 and SBS92) and pack-years in 386 LUAD and LUSC tumours from patients with a smoking history. Pearson’s correlation tests were used. c, Cumulative percentage of all LUAD tumours with SBS4 detection or lack of SBS4 detection with increasing maximum years smoked. A total of 223 tumours were analysed. d, Comparison of pack-years between patients with LUAD with different SBS4 detection statuses in their tumour. A total of 215 patients were included. Each data point represents a patient with LUAD and an ever-smoker. e, The percentage of LUAD tumours harbouring EGFR mutations, RET–ROS1–ALK oncogenic fusions and MET exon-skipping events in patients who never smoked and in patients who have smoked split by SBS4 detection status. A total of 248 tumours were included. f, Frequency of tumours in the TRACERx 421 cohort located in each lung lobe and the median number of truncal SBS4-associated mutations for tumours located in each lung lobe. A total of 358 LUAD and LUSC tumours from ever-smokers were included. LLL, left lower lobe; LUL, left upper lobe; RML, right middle lobe; RLL, right lower lobe; RUL, right upper lobe. The schematic in f was created using BioRender (https://biorender.com).