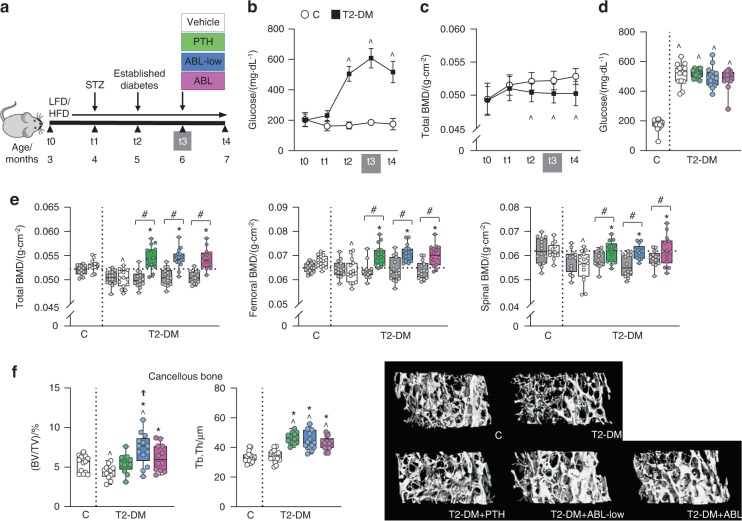
Fig. 1.
PTH and both doses of ABL restored BMD and increased cancellous bone in diabetic mice. a Study design depicting the preclinical T2-DM model. Male C57BL/6 mice were fed a low-fat diet (LFD) or a high fat diet (HFD) starting at t0 until the end of the experiment. At t1, HFD-fed mice were injected with streptozotocin (STZ) (T2-DM) and LFD-fed mice, with buffer (C). At t2, blood glucose was measured to confirm DM, and following an additional month to fully develop the bone disease at t3, mice were administered with vehicle, PTH or ABL daily for 4 weeks (t4). Longitudinal analysis showing the effect of DM on b blood glucose, and c total bone mineral density (BMD). d Glucose levels after treatment (at t4). e Total, femoral and spinal BMD before treatment (at t3, grey bars) and after treatment (at t4) with vehicle (white bars), PTH (green bars) or ABL (blue and pink bars). f Micro-CT analysis of femur cancellous bone: trabecular bone volume/tissue volume (BV/TV) and trabecular thickness (Tb.Th), after treatment with PTH or ABL and representative images. n = 12–15 mice per group. Data are presented as box & whisker plots where each dot represents a mouse. ^P < 0.05 versus C mice by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Dunnet’s correction; *P < 0.05 versus T2-DM mice treated with vehicle; and #P < 0.05 versus t3, by one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey’s correction