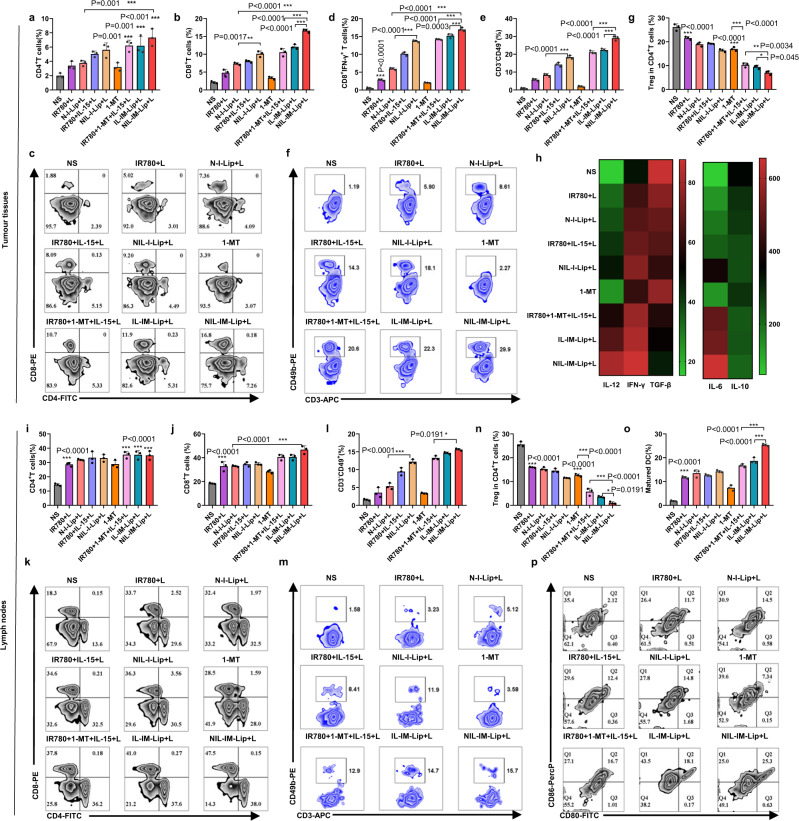
Fig. 7. Effects of NIL-IM-Lip + L treatment on the simultaneous coactivation of CTLs and NK cells and the reversion of the suppressive conditions in the TLIME in the B16F10 model.
a–c Flow cytometric analysis of intratumoural CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells. d Flow cytometric analysis of the infiltration of CTLs into tumours (n = 3 biologically independent experiments per group). e, f Flow cytometric analysis of NK cell infiltration into the tumours (n = 3 biologically independent experiments per group). g Flow cytometric analysis of the infiltration of Treg cells gated on CD4+ lymphocytes in the tumours (n = 3 biologically independent experiments per group). h Quantitative ELISA analysis of the cytokines in the tumour tissues from mice treated with different formulations (n = 3 biologically independent experiments per group). i–k Flow cytometric analysis of the infiltration of CD4+ T cells and CD8+ T cells in the LNs (n = 3 biologically independent experiments per group). l, m Flow cytometric analysis of NK cell infiltration into LNs (n = 3 biologically independent experiments per group). n Flow cytometric analysis of the infiltration of Treg cells gated on CD4+ lymphocytes in the LNs (n = 3 biologically independent experiments per group). o, p Flow cytometric analysis of DC infiltration in LNs (n = 3 biologically independent experiments per group). Data are presented as mean values ± SD. Statistical significances were calculated by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s post hoc test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. N-I-Lip+L NGR-IR780-Lip+Laser, NIL-I-Lip+L NGR/IL-15-IR780-Lip+Laser, IL-IM-Lip+L IL-15-IR780/1-MT-Lip+Laser.