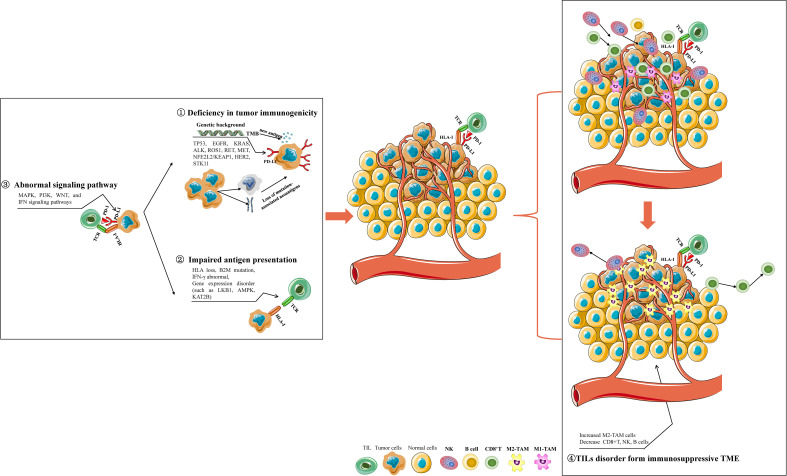
Figure 4.
The mechanisms involved in immunotherapy resistance of NSCLC. Deficiency in tumor immunogenicity: various drive gene mutations affect PD-L1 expression, TMB, and tumor-specific neoantigen formation; Impaired antigen presentation: HLA loss, B2M mutation, IFN-γ signaling dysregulation, and some genes disorder; Abnormal signaling pathway: abnormal MAPK, PI3K, WNT, and IFN signaling pathways may influence tumor immunogenicity and antigen presentation; Abnormal activity and infiltration of immune cells in NSCLC TME: NSCLC TME enriched with increased M2 macrophages, decreased B cells, and NK cells form an immunosuppressive TME to resist the initiation of antitumor immunity. Some gene expression disorders or mutations in NSCLC cells can impair the activity, tumor-cell-killing function, proliferation, and infiltration of CD8+ T-cells in TME, which contribute to exhausted CD8+ T-cells for immunotherapy resistance.