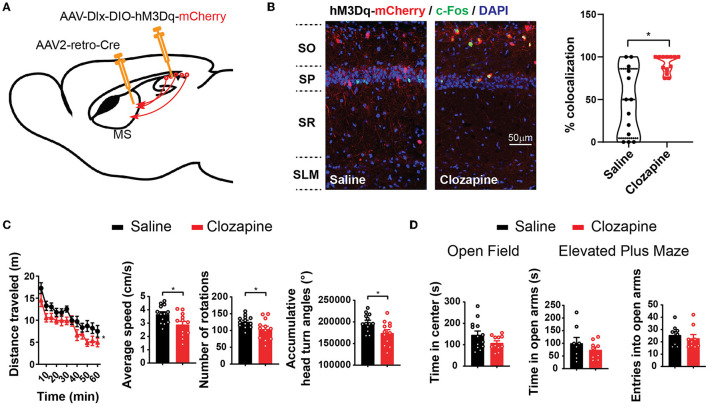
Figure 3.
Activation of septum-projecting interneurons reduces locomotion. (A) Expression of hM3Dq in septum-projecting hippocampal GABAergic interneurons by AAV injections. (B) Intraperitoneal injections of clozapine (0.1 mg/kg), a ligand of hM3Dq, increased activity of septum-projecting hippocampal GABAergic interneurons measured by double labeling of c-Fos (green) and mCherry (red) (saline, n = 13 sections, total 62 cells from two mice; clozapine, n = 13 sections, total 73 cells from two mice) (Mann–Whitney U-test, *p < 0.05). (C) Activation of the septum-projecting hippocampal GABAergic interneurons with clozapine decreased mouse locomotion measured by the distance traveled in the open field, number of rotations, and accumulative head turn angles [two-way ANOVA, F(1,23) = 6.35, p < 0.05; Two-tailed t-test, *p < 0.05]. (D) Activation of the septum-projecting hippocampal GABAergic interneurons did not change time spent in the center of the open-field test (two-tailed t-test, p = 0.1), time spent in the open arms (two-tailed t-test, p = 0.31), and the number of entries into the open arms of the elevated plus maze test (two-tailed t-test, p = 0.55) (open field: saline: n = 13; clozapine: n = 11. Elevated plus maze: saline: n = 8; clozapine: n = 9).