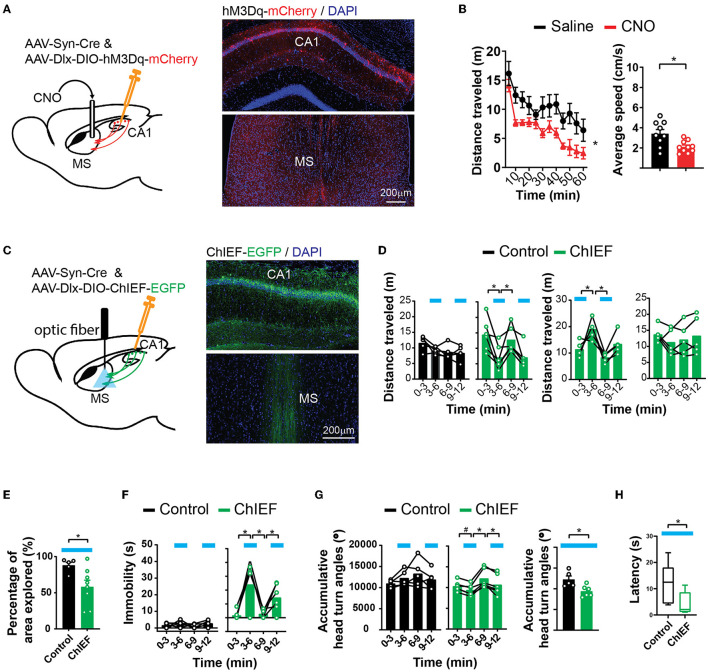
Figure 4.
Activation of hippocampal inhibitory projections to the MS reduces locomotion. (A) Pharmacogenetic activation of the hippocampal inhibitory inputs to the MS with local infusion of CNO in the MS. (B) CNO decreased locomotion in the open field as measured by distance traveled [two-way ANOVA, F(1,17) = 9.00, *p < 0.05] and average speed (two-tailed t-test, *p < 0.05) (saline, n = 9 mice; CNO, n = 10 mice). (C) Optogenetic activation of the hippocampal inhibitory inputs to the MS by light. An excitatory channelrhodopsin, ChIEF, was expressed in the hippocampal GABAergic neurons with AAVs in the “ChIEF” mice. Control mice received AAVs expressing EGFP only. (D–H) Light delivered to the MS (indicated by blue bars) decreased mouse locomotion measured by distance traveled (D), percentage of the open-field area the mice explored (E), immobility (F), accumulative angles of head turns (G), and latency to reach a low speed (H). [(D) Two-way ANOVA. Left ChIEF group, light, F(1,5) = 30.42, p < 0.05; Right ChIEF group, light, F(1,4) = 10.15, p < 0.05; Tukey's multiple comparison test, *p < 0.05. (E) Two-tailed t-test, *p < 0.05. (F) Left two-way ANOVA. Control group, light, F(1,4) = 5.409, p = 0.08; ChIEF group, light, F(1,5) = 10.57, p < 0.05; Tukey's multiple comparison test, *p < 0.05. (G) Left two-way ANOVA. Control group, Light, F(1,4) = 0.03, p = 0.86; ChIEF group, light, F(1,5) = 22.01, p <0.05; Tukey's multiple comparison test, *p < 0.05; Right two-tailed t-test, *p < 0.05. (H) Mann–Whitney U-test, *p < 0.05.] (Control, n = 5 mice; ChIEF, n = 6 mice).