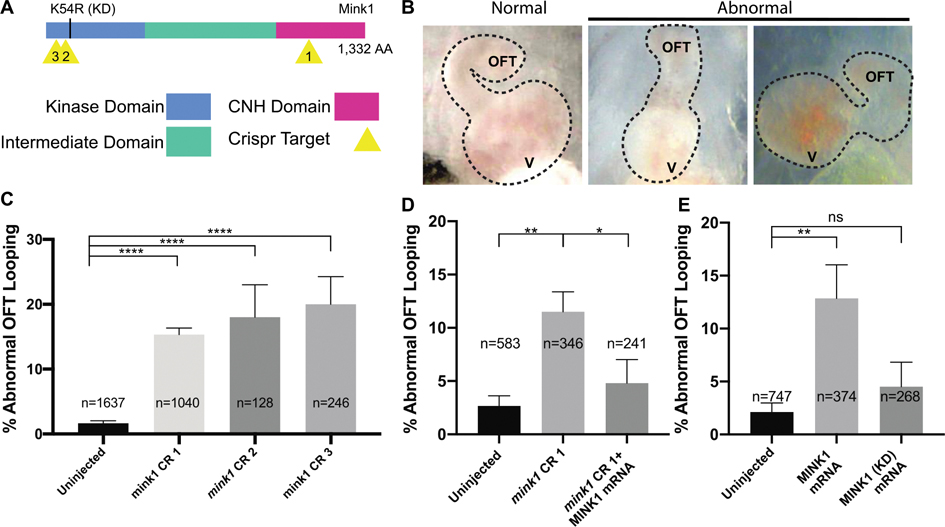
Figure 1: Loss of mink1 Induces Abnormal Heart Development.
A) Schematic of Xenopus tropicalis Mink1 protein domains, site of kinase-dead (KD) mutation, and Crispr target sites (yellow). Protein homology between human and X. tropicalis Mink1 is 76%. B) Representative images of Xenopus tropicalis normal and abnormal cardiac outflow tracts (ventral views with anterior at top) at stage 45. OFT: outflow tract, V: ventricle. C) Quantification of abnormal cardiac outflow tract looping in mink1 crispants. 5, 3 and 12 biological replicates included for CRISPRs 1, 2 and 3, respectively. D) Rescue of mink1 depletion cardiac looping phenotype with human MINK1 mRNA. 5 biological replicates. E) Quantification of abnormal cardiac OFT looping in embryos with overexpression of wild-type and kinase-dead human MINK1 RNA. Lower dose of MINK1 RNA used for rescue than for overexpression (see Methods). 7 and 4 biological replicates included. P < 0.0001= ****, p < 0.005= **, p < 0.05= * by two-tailed T-test.