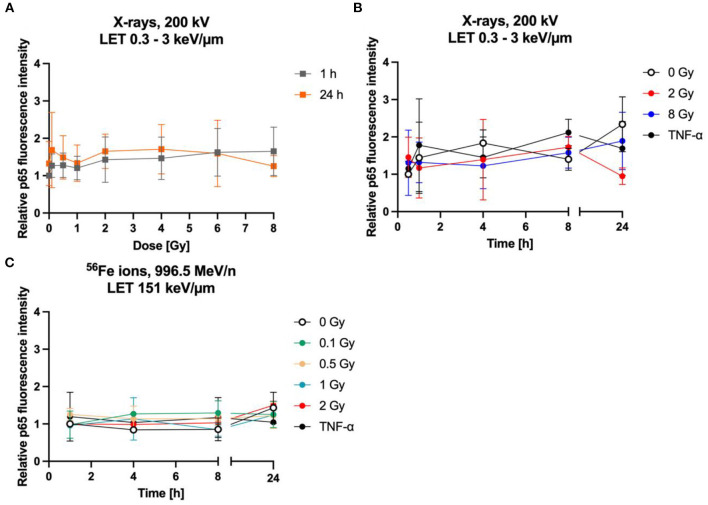
Figure 9.
The NF-κB pathway is not activated by radiation exposure in astrocytes. Astrocytes were exposed to X-rays (A, B) or iron ions (C) and fixed at time points up to 24 h after irradiation for immunofluorescence staining of the NF-κB subunit p65. (A) Dose effect curves of activation of NF-κB pathway (p65) after exposure to X-rays (n = 6). (B) The relative fluorescence intensity of p65 in the nucleus area for different doses of X-irradiation over a time period up to 24 h, showing a basal activity of the NF-κB pathway but no further significant induction by radiation exposure or incubation with TNF-α. The samples were compared via Tukey's multiple comparison test, based on a sample size of n = 3. (C) Exposure to different doses of 56Fe ions (LET 151 keV/μm, 996.5 MeV/n) did not induce any further activation of NF-κB pathway (n = 2). The relative fluorescence intensity of p65 in the nucleus area was calculated by normalizing the raw integrated density for each treatment to the raw integrated density of the untreated control at the earliest time point that was investigated. Data are shown as mean ± SD.