Fig. 1 |. Fungal diversity.
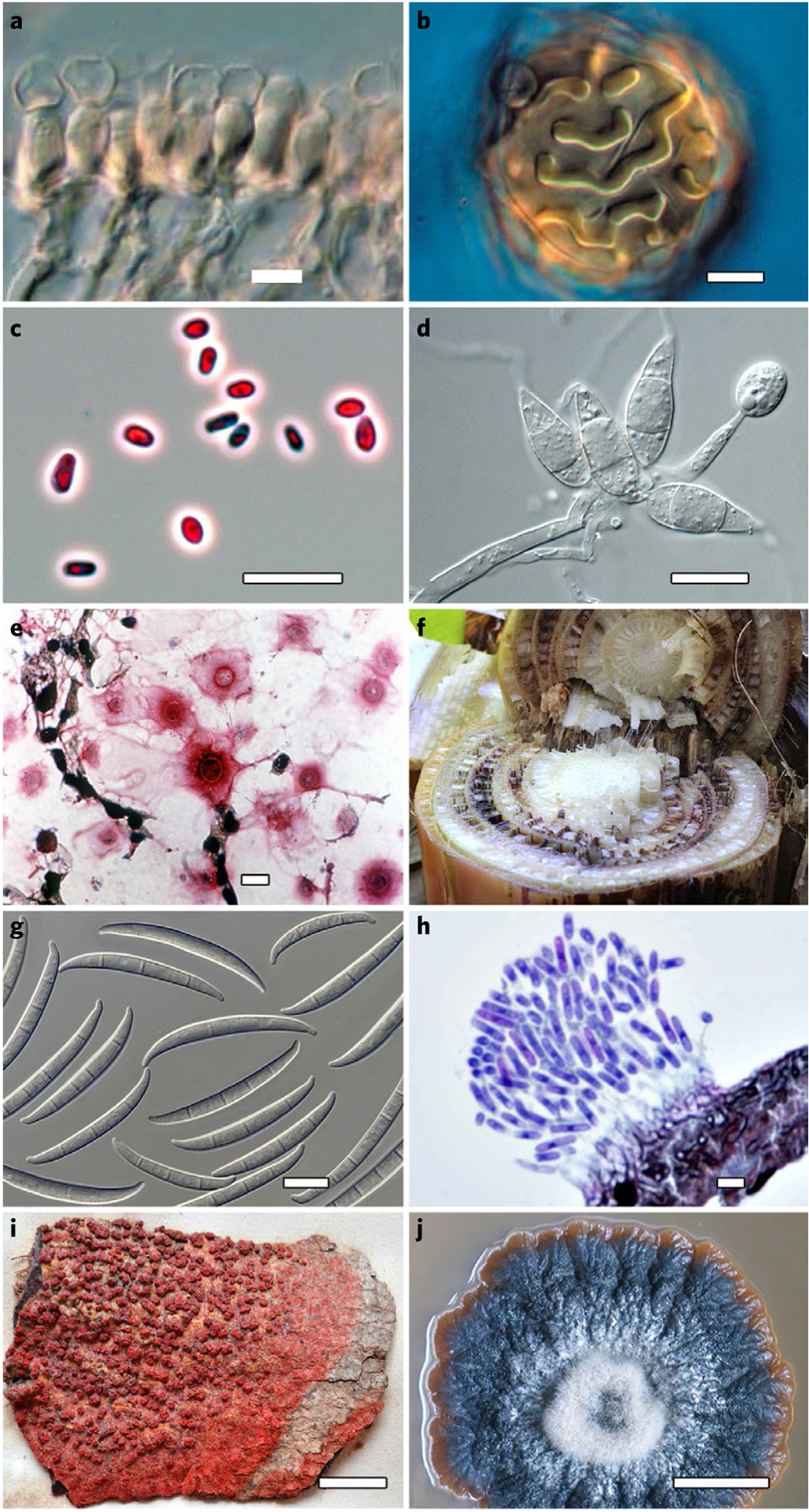
Although Fungi and fungus-like organisms exhibit striking phenotypic diversity, accurate and precise identification often requires molecular approaches or specific tools such as metabolic profiling owing to widespread cryptic diversification and a lack of diagnostic features in microscopic vegetative structures. a, Albugo laibachii (Oomycota) sporogenous hyphae. b, Albugo candida oospore. c, Candida auris cells. d, Pyricularia oryzae conidiophore with conidia. e, Cryptococcus neoformans cells in tissue. f, Banana plant infected with fusarium wilt. g, Fusarium odoratissimum macroconidia. h, Colletotrichum siamense section of acervulus. i, Trypethelium purpurinum (also known as Marcelaria purpurina) physical type specimen. j, Chaetocapnodium tanzanicum culture. Credit: photographs courtesy of Young-Joon Choi (a,b), Nani Maryani (f,g), Min Fu (h) and Jafar Abdollahzadeh (j). Scale bars, 10 μm (a–e, g and h) or 10 mm (i and j).
