Figure 1.
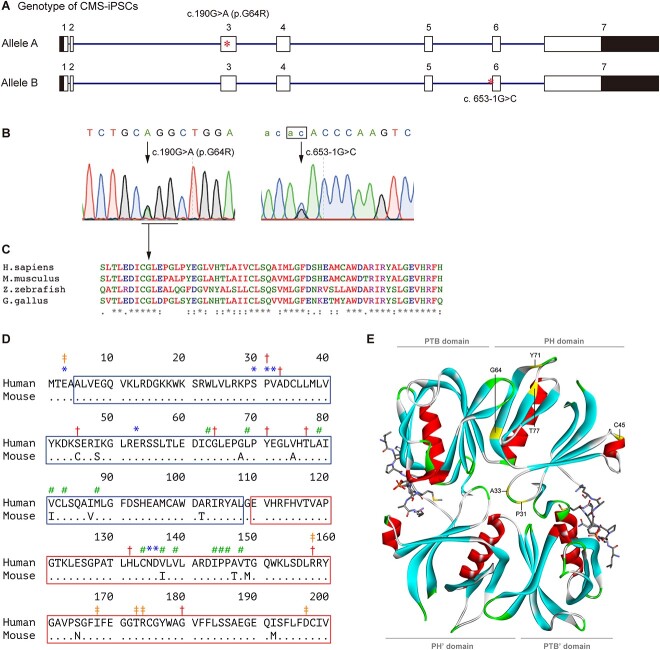
Mutations in DOK7. (A) Schematic of DOK7 gene (NM_173660.5) showing the location of mutations (red asterisks). The 5′ and 3′ untranslated regions are shown in black. (B) Sequencing chromatograms showing heteroallelic mutations. An invariant ‘ag’ dinucleotide at the 3′ end of intron 5 is indicated by a box. (C) Alignment of DOK7 proteins across species. Alignment was performed using ClustalW2 (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/). Glycine at codon 64 (GGG) is conserved across species, and is changed to arginine (AGG). (D) Alignment of the PH (blue box) and PTB (red box) domains of human and mouse DOK7 (14). Identical residues are indicated by dots. *Residues for DOK7 dimerization. #Residues for PH-PTB interaction. ‡Residues for binding to MuSK pTyr533. †Residues mutated in CMS. Note that the mutated serine at codon 45 in human is cysteine at codon 45 in mouse. (E) Crystal structure of the PH and PTB domains of mouse DOK7 dimer (ribbons) and MuSK phosphopeptides (sticks) (14). Six residues mutated in CMS in the PH domain are indicated in the upper DOK7. Domains in the lower DOK7 are indicated by apostrophe.