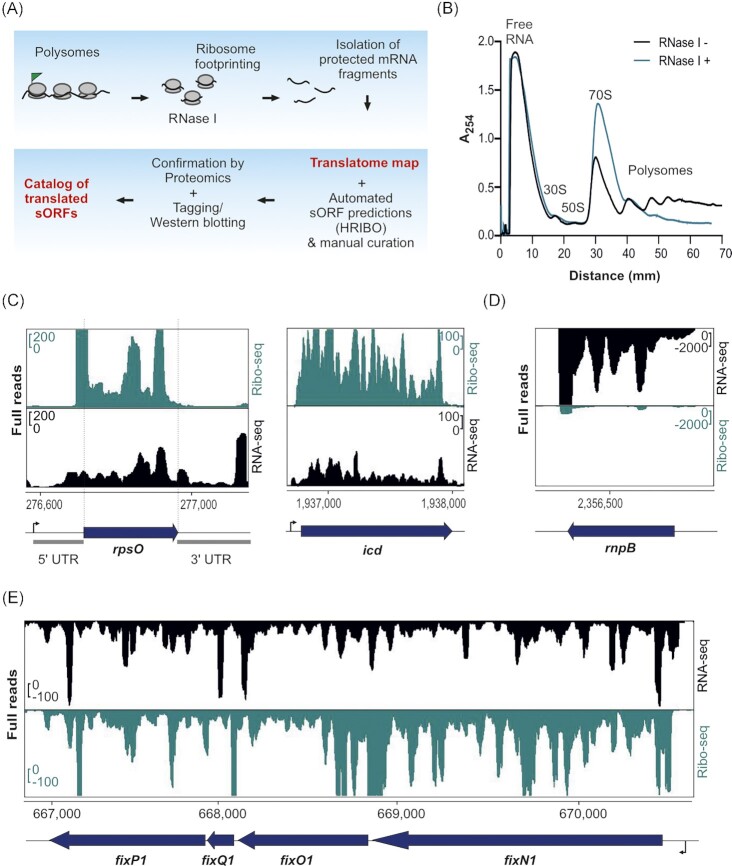
Figure 1.
Establishment of ribosome profiling (Ribo-seq) for Sinorhizobium meliloti. (A) Schematic Ribo-seq workflow to map the S. meliloti 2011 translatome. Translating ribosomes (indicated by the polysome fraction) were first captured on the mRNAs. Unprotected mRNA regions were digested by RNase I, converting polysomes to monosomes. Approximately 30-nt-long footprints protected by and co-purified with 70S ribosomes were then subjected to cDNA library preparation and deep sequencing to identify the translatome under the used conditions. The small proteome was identified using HRIBO automated predictions and manual curation. Mass spectrometry and Western blot analysis of recombinant, tagged small open reading frame (sORF)-encoded proteins were used to validate the translated sORFs. (B) Sucrose gradient fractionation of the lysates. Cells were harvested at the exponential growth phase by a fast-chilling method to avoid polysome run-off. RNase I digestion led to enrichment of monosomes (70S peak in the green profile) in contrast to the untreated sample (Mock, black profile). Absorbance at 254 nm was measured. (C) Integrated genome browser screenshots depicting reads from Ribo-seq and RNA-seq libraries for two annotated ORFs: rpsO encoding ribosomal protein S15 and icd encoding isocitrate dehydrogenase. They show read coverage enrichment in the Ribo-seq library along their coding parts in contrast to the RNA-seq library but not in the ribosome-non-protected regions (UTRs). The UTRs of rpsO are marked. (D) Read coverage for rnpB corresponding to the housekeeping RNase P RNA. Reads are mostly restricted to the RNA-seq library, suggesting that this RNA is not translated. (E) The fixN1OQP operon shows read coverage in both the RNA-seq library and Ribo-seq library, the latter indicating that this operon contains translated genes. Genomic locations and coding regions are indicated below the image. Bent arrow indicates the transcription start site based on (Sallet et al. 2013).