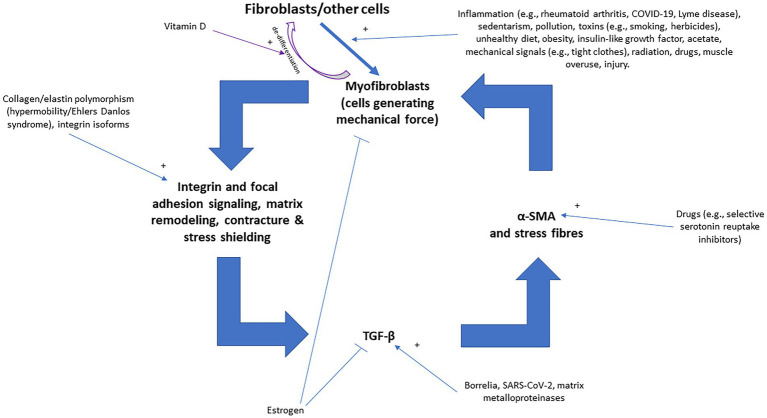
Figure 4.
The positive feedback loop of fascial armoring (fascial rigidity and tensegrity tension) with inputs into the vicious cycle of myofibroblasts [adapted for long COVID-19 from Figure 3 in Plaut (2023) (7)]. Fibroblasts, adipocytes, and other cell-types can differentiate to myofibroblasts (the intermediate proto-myofibroblast phenotype is not shown here). Empirical studies show that various factors influence fibroblast-to-myofibroblast differentiation (and epithelial to mesenchymal transition), including immobility, infection/inflammation, diet, herbicides, drugs, epi/genetics, etc. (4, 138, 144). Once myofibroblasts activity is initiated, a positive feedback loop can stimulate and maintain fascial armoring, i.e., lead to a chronic fascial bio-tensegrity pathology driven by a myo/fibroblast network of contracting cells in connective tissue. Any imbalance in the constant interplay of the various promoting/inhibiting factors in this loop will regulate the course of the disease. Macrophages and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition can also lead to (or differentiate to) myofibroblasts but are not depicted in this scheme for the purpose of simplicity. Open arrows with a plus sign indicate upregulation/stimulation, closed arrows indicate downregulation/inhibition. TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; α-SMA, alpha smooth muscle actin.