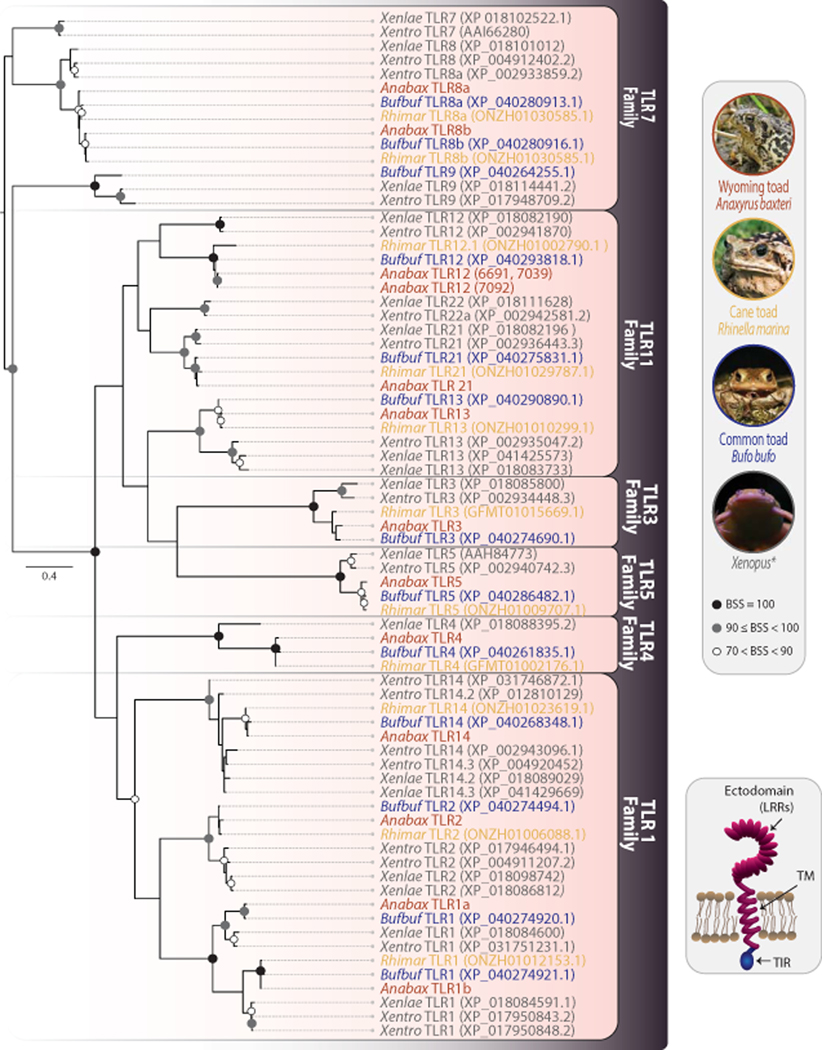
Fig. 2. Wyoming toad transcriptomes reveal 13 toll-like receptor genes.
Phylogenetic tree comparing TLR TIR domains of three Wyoming toads to those in five other ranid species, including two additional bufonids. Sequences are from Wyoming toad (Anabax), common toad (Bufbuf), cane toad (Rhimar), Xenopus laevis (Xenlae) and Xenopus tropicalis (Xentro). Sequence identifiers for Wyoming toad TLRs are provided in Supplemental Table S3. If available, GenBank or Xenbase identifiers are included in the figure with sequence names. As TLR LRR ectodomains are typically variable between species, the more conserved TIR domains were employed for phylogenetic analyses (Quiniou et al. 2013; Boudinot et al. 2014; Wcisel et al. 2017). Wyoming toads express TLRs in all six of the major TLR families with identical or nearly identical sequences across the three individuals. Circles at nodes indicate bootstrap support values (BSS) with filled black circles indicating BSS=100, gray circles indicating BSS values equal to or greater than 90 but less than 100, and white circles indicating BSS values greater than 70 but less than 90. Scale bar indicates substitutions over time.