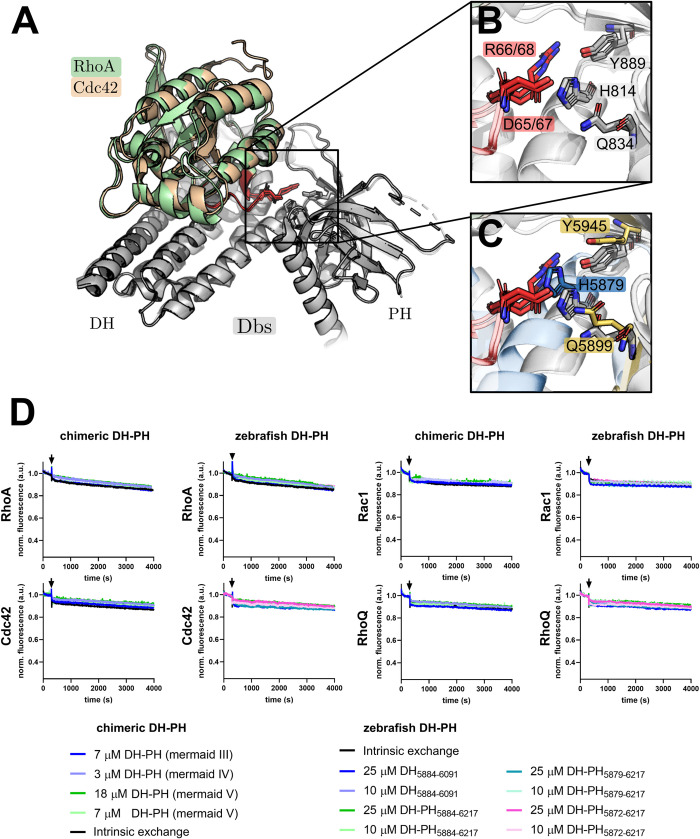
Fig 3. Influence of the obscurin PH domain on nucleotide exchange activity.
A-C, Structural determinants of nucleotide exchange activity in Trio-subfamily GEFs. A, the aligned structures of Dbs bound to RhoA (PDB-ID: 1LB1) and Cdc42 (PDB-ID: 1KZ7) show a contact between the DH-PH domain interface and the switch II region (red) of the respective substrate GTPase. B, a closer view of this contact shows a polar interaction between a switch II arginine and aspartate (red) and three conserved residues of the GEF (grey), two of which belong to the PH domain (Tyr889 and Gln834). C, Alignment of the predicted structure of the human obscurin DH-PH to the Dbs RhoA/Cdc42 complex shows that the corresponding obscurin residues are in a similar position as in the Dbs/substrate GTPase complexes. D, Guanosine nucleotide exchange factor activity of chimeric and zebrafish obscurin RhoGEF fragments towards RhoA, Cdc42, Rac1 and RhoQ/TC10. Black arrows indicate addition of buffer/GEF/EDTA. Data represent mean of n = 2–3 experiments. See Fig 2 for controls (experiments have been performed simultaneously in a multi-well plate reader).