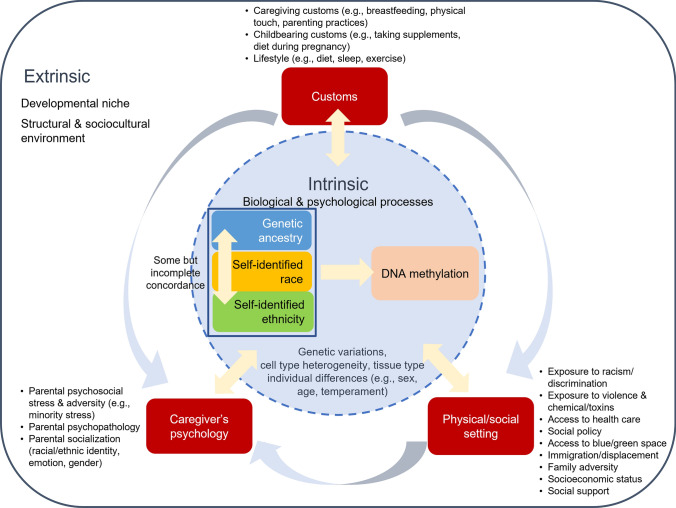
Fig. 2.
Integrative framework illustrating how intrinsic and extrinsic environmental factors tied to self-identified race and ethnicity contribute to DNA methylation (DNAm), which has the potential to alter gene expression and influence downstream biological functions associated with health and diseases. The circle represents an individual, with all the components inside the circle as intrinsic factors. The three main constructs—genetic ancestry, self-identified race, and self-identified ethnicity—are highlighted by the colored boxes, with other intrinsic factors that may influence DNAm encompassed within the circle. The extrinsic part is made up of both developmental niche and other structural and sociocultural environmental factors shown in red boxes. The developmental niche surrounding the individual consists of three subsystems, i.e., physical/social settings, customs, and caregiver’s psychology, which bring culture into their daily experience. Specific factors under each of the three subsystems of the developmental niche associated with DNAm and self-identified race and ethnicity are listed. The arrows between the three subsystems as well as those between the extrinsic and intrinsic factors represent their constant interactions and their contributions to the relations of race, ethnicity, and genetic ancestry with DNAm