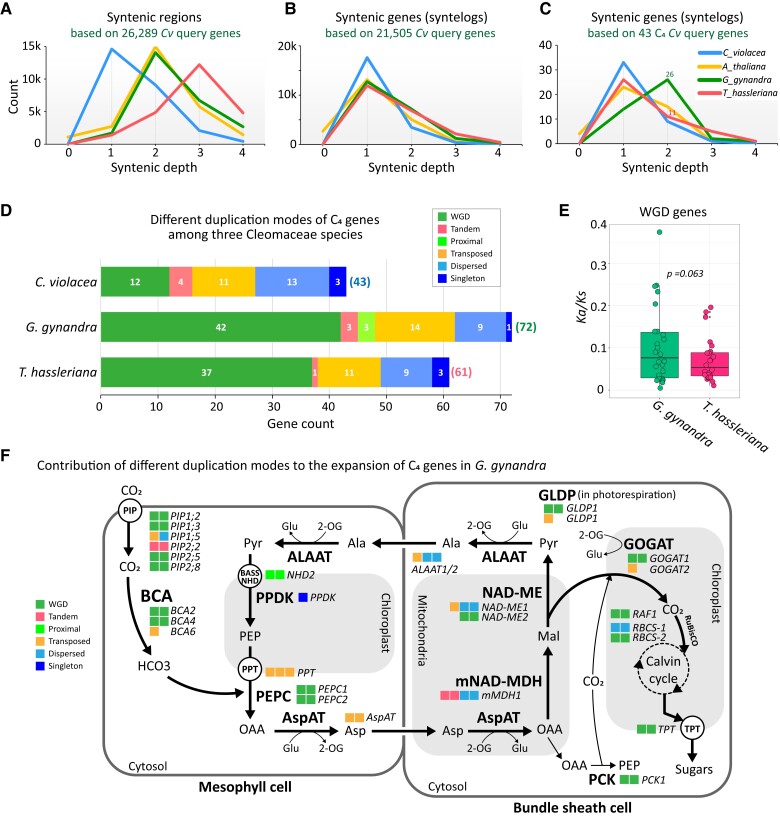
Figure 6.
Contribution of gene duplication on the evolution of C4 photosynthesis in Cleomaceae. A–C, Plots of syntenic regions and genes analyzed by SynFind using all C. violacea genes and a set of 43 genes known to be involved in C4 photosynthesis, searched against the genomes of A. thaliana, G. gynandra, and T. hassleriana. For each panel, genes that showed no syntenic regions or syntelogs in both G. gynandra and T. hassleriana were excluded. D, Number of syntelogs identified in each species corresponding to the 43 C4 genes in the C. violacea genome. Modes of gene duplication were obtained from the Dupgene_finder results presented in Figure 4. E, Ka/Ks ratios of WGD-derived gene pairs among the syntelogs identified in G. gynandra and T. hassleriana as shown in (D). The P-value was calculated by Student's two-sided t-test. F, Expansion pattern and duplication modes of gene families involved in C4 photosynthesis. Each box represents one gene copy. Box colors indicate duplication mode that are shown at the bottom left corner. The expanded gene copies were derived from both SynFind analysis and Dupgene_finder results (in Figure 4). BCA (BETA CARBONIC ANHYDRASE), PEPC (PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE CARBOXYLASE), AspAT (ASPARTATE AMINOTRANSFERASE), mMDH (MITOCHONDRIAL MDH), NAD-ME (NAD-DEPENDENT MALIC ENZYME), ALAAT (ALANINE AMINOTRANSFERASE), PPDK (PYRUVATE ORTHOPHOSPHATE DIKINASE), PCK (PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE CARBOXYKINASE), GOGAT (GLUTAMINE OXOGLUTARATE AMINOTRANSFERASE), GLDP (GLYCINE DECARBOXYLASE P-PROTEIN), TPT (TRIOSE-PHOSPHATE⁄PHOSPHATE TRANSLOCATOR), PIPs (PLASMA MEMBRANE INTRINSIC PROTEIN), RBCS (RUBISCO SMALL SUBUNIT), RAF1 (RUBISCO ACCUMULATION FACTOR1), OAA (OXALOACETATE), Asp (ASPARTIC ACID), Mal (MALATE), Pyr (PYRUVATE), Ala (ALANINE), PEP (PHOSPHOENOLPYRUVATE), Glu (GLUTAMATE), and 2-OG (2-OXOGLUTARATE).