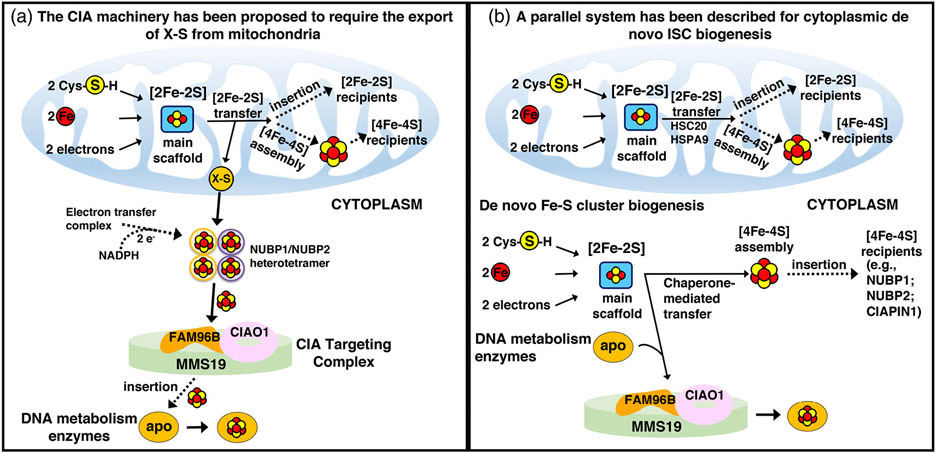
FIGURE 11.
Alternative proposed models of cytoplasmic Fe-S cluster biogenesis. In the schematic on the left, assembly of cytoplasmic Fe-S clusters begins in mitochondria with components of the early Fe-S cluster biogenesis machinery synthesizing a sulfur-containing precursor (X-S) that is subsequently exported to the cytosol by the ABC transporter Atm1 (ABCB7 in human) and utilized by the CIA machinery for the biosynthesis of [4Fe-4S] clusters upon the main hetero-tetrameric complex composed of NUBP1 and NUBP2.131 In the model on the right, alternative isoforms of the core early Fe-S cluster biogenesis factors are present in the cytosol of mammalian cells where they initiate de novo assembly of [2Fe-2S] clusters on the main cytosolic scaffold protein ISCU1. A dedicated chaperone/co-chaperone system, consisting of HSPA9 and HSC20 (aka HSCB), either facilitates direct Fe-S cluster transfer to a subset of recipient cytosolic proteins (e.g., CIAPIN1, NUBP1, and NUBP2), or mediates transfer of Fe-S clusters to enzymes involved in DNA metabolism through direct binding of HSC20 to the LYR motif of the CIAO1 component of the CIA-targeting complex.128 Adopted from139