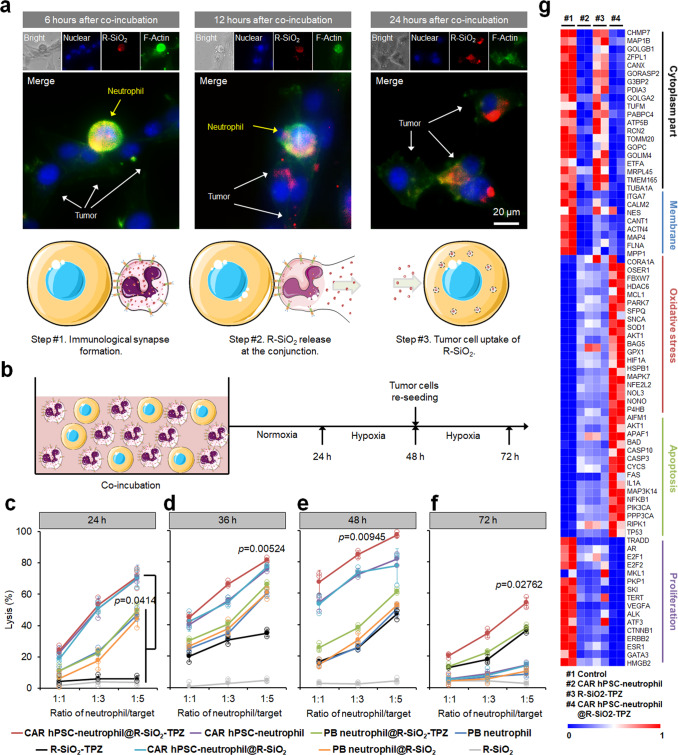
Fig. 4. CAR-neutrophils loaded with R-SiO2-TPZ nanoparticles effectively kill glioblastoma cells.
a Representative images of immunological synapses indicated by polarized F-actin accumulation at the interface between CAR-neutrophils and tumor cells at 6, 12 and 24 h were shown. R-SiO2-TPZ nanoparticles released from CAR-neutrophils upon tumor cell phagocytosis were up-taken by tumor cells. Triplicates were performed independently. b Schematic of neutrophil-mediated anti-tumor cytotoxicity assay. Cytotoxicity against U87MG glioblastoma cells were performed at different ratios of neutrophil-to-tumor target using indicated neutrophils at 24 h (c), 36 h (d), 48 h (e), and 72 h (f). n = 3 biologically independent samples. Data are represented as mean ± SD, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA). g Bulk RNA sequencing analysis was performed on U87MG cells under various conditions. Heatmap shows expression levels of selected cytoplasm, membrane, oxidative stress, apoptosis, and proliferation-related genes in the indicated glioblastoma cells. n = 2 biologically independent samples. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.