Figure 5.
Spontaneous or colitis-associated tumor formation
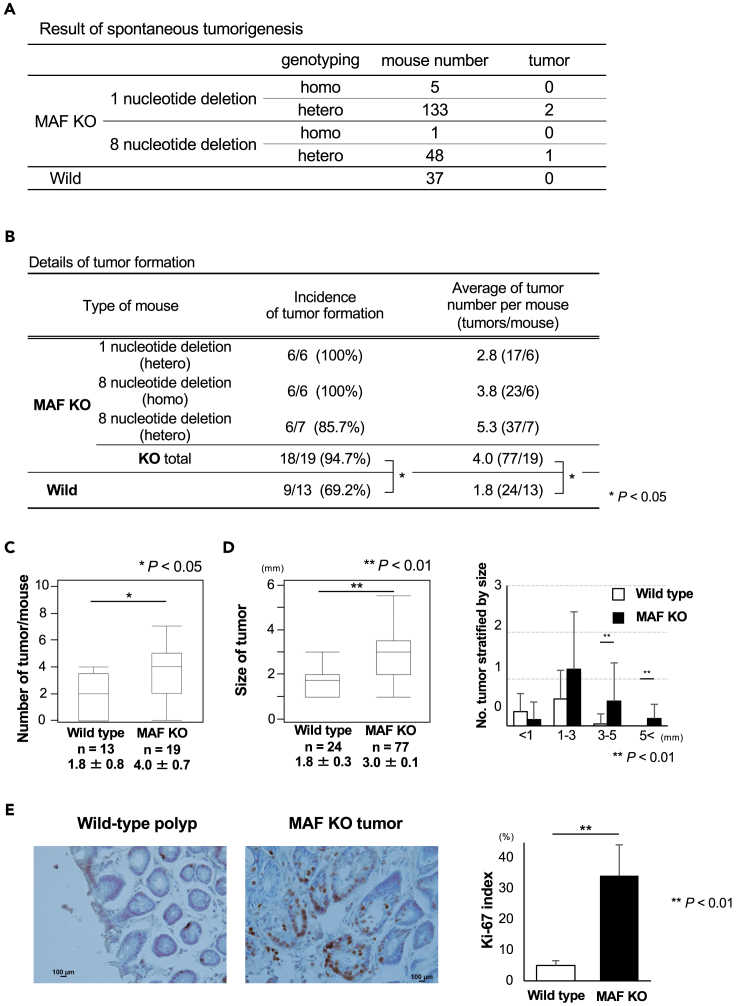
(A) Tumors that spontaneously occurred are summarized. Only three tumors were generated in c-MAF KO mice around 2 years after birth.
(B) Details of colitis-associated tumor formation; n = 32 mice (19 c-MAF KO and 13 wild type). The majority of c-MAF KO mice (18 of 19, 94.7%) developed colorectal tumors whereas 9 of 13 (69.2%) of wild-type mice did. The incidence of tumor formation was significantly higher in c-MAF KO mice. The average tumor number in each group is also shown.
(C) Number of tumors per mouse. c-MAF KO mice produced significantly more tumors than did wild-type mice.
(D) Tumor size was significantly larger in c-MAF KO mice compared with wild-type mice. When stratified by tumor diameter at 1, 3, and 5 mm, c-MAF KO mice had significantly more tumor formation >3 mm.
(E) Immunohistochemical staining for Ki-67 in tumors. c-MAF KO tumors had a significantly higher Ki-67 index as compared with wild-type tumors. Scale bars: 100 μm. Data are expressed as mean ± standard deviation, or the median and interquartile range (IQR). Statistical differences were analyzed using Student’s t test. The incidence of tumor formation and the size of tumor in c-MAF KO mice and wild-type mice were analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01. KO, knock out; WT, wild type.