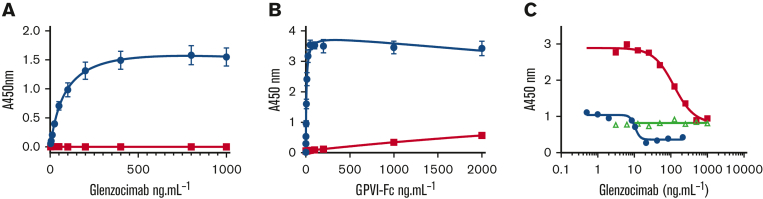
Figure 6.
Truncation of GPVI Δ129 to 136 disrupts the epitope of glenzocimab. GPVI-Fc Δ129 to 136 was compared with GPVI-Fc regarding interactions with glenzocimab in solid-phase assays. (A) Dose-dependent binding of glenzocimab to immobilized GPVI-Fc (blue circles) and GPVI-Fc Δ129 to 136 (red squares). The EC50 value of GPVI-Fc was of 85 ng.mL−1 (1.88 nM), in line with the KD value. No binding between glenzocimab and GPVI-Fc Δ129 to 136 could be observed even at 1 μg.mL−1, which is more than 10-fold the EC50 of GPVI-Fc. (B) Dose-dependent binding of GP-VI-Fc (blue circles) and GPVI-Fc Δ129 to 136 (red squares) to immobilized glenzocimab confirms defective interactions between glenzocimab and GPVI-Fc Δ129 to 136. Results are mean ± standard error of the mean of 3 experiments performed in triplicate. (C) Inhibition of GPVI-Fc binding to immobilized collagen by increasing concentrations of glenzocimab. Binding of GPVI-Fc at 2 μg.mL−1 (blue circles) or at 20 μg.mL−1 (red squares) to collagen was dose-dependently inhibited by glenzocimab with IC50 values of 10.25 and 113.7 μg.mL−1, respectively. In contrast, glenzocimab at 20 μg.mL−1 had no effect on the binding of GPVI-Fc Δ129 to 136 to collagen (green triangles).