FIGURE 5.
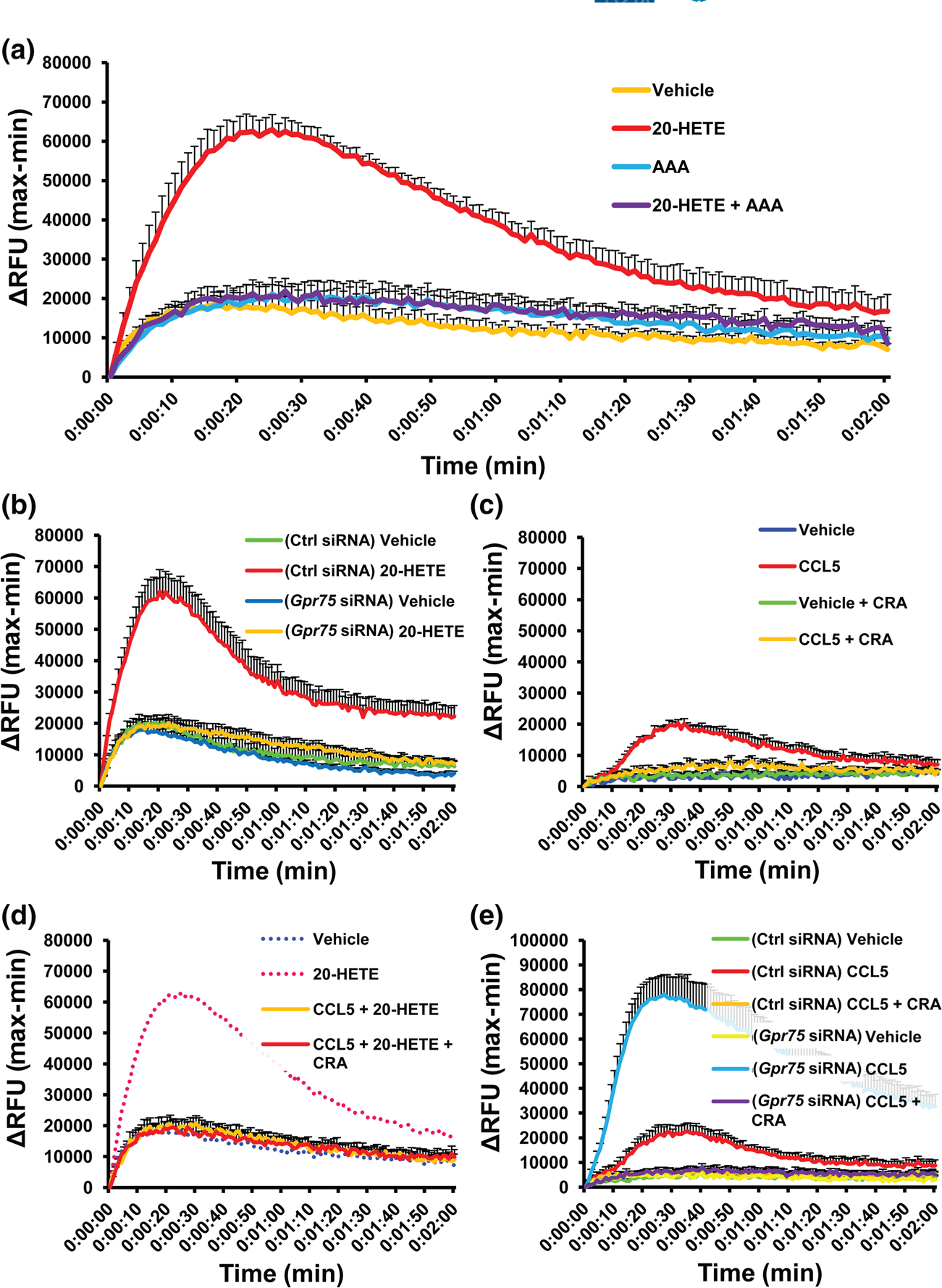
20-HETE, but not CCL5, increases intracellular calcium (iCa2+) via GPR75 in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). FLIPR Calcium 6 assays of HUVECs treated with; (a) vehicle (ethanol), 20-HETE (1 nM) and co-treatment of 20-HETE (1 nM) with AAA (1 nM), a 20-HETE receptor antagonist; (b) GPR75 knockdown in HUVECs abolishes 20-HETE-mediated increases in iCa2+. Effect of 20-HETE (1 nM) on intracellular calcium in control (Ctrl) and GPR75 siRNA-treated HUVECs. (c) CCL5 increases iCa2+ via its chemokine receptors. Effects of vehicle (PBS) and CCL5 (0.1 nM) in the presence and absence of CCL5 receptor antagonists (CRA) (BX471 targeting CCR1 [25 nM], SB328437 targeting CCR3 [80 nM] and DAPTA targeting CCR5 [20 nM]); (d) CCL5 blocks 20-HETE-stimulated increases in iCa2+. Effects of pretreatment of CCL5 (0.1 nM) ± CRAs followed by 20-HETE (1 nM). (e) Gpr75 knockdown intensifies CCL5 (RANTES)-mediated changes in iCa2+ in HUVECs. Effect of CCL5 (0.1 nM) on intracellular calcium in control (Ctrl) or GPR75 siRNA-treated HUVECs. Data shown are means ± SEM; n = 6
