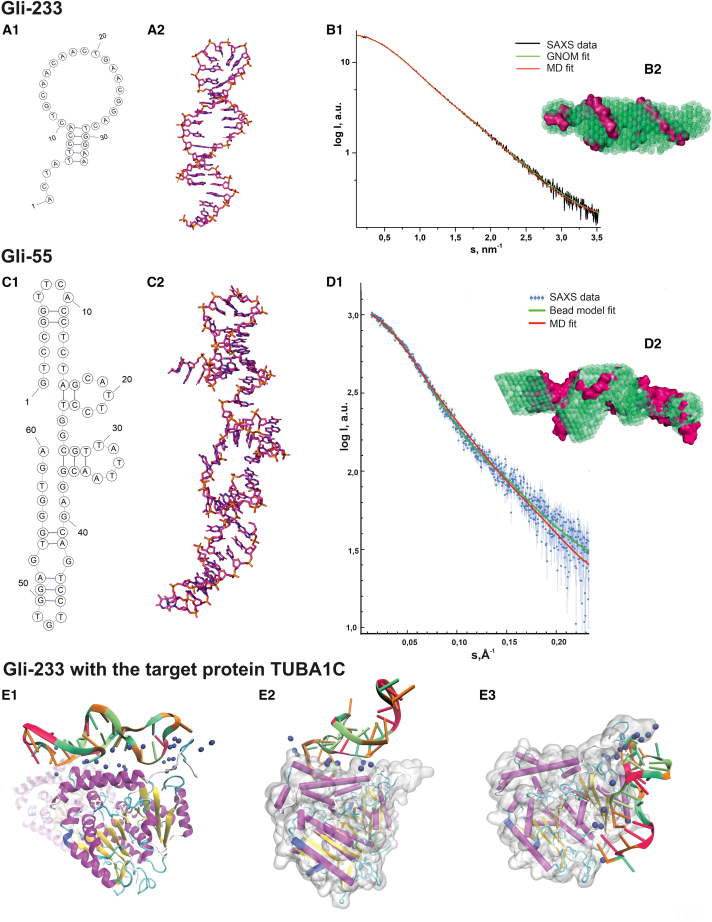
Figure 3.
Molecular design of a 3D structure of Gli-233 and Gli-55 aptamers and Gli-233 binding to a protein target
(A) Structures of the Gli-233 aptamer: secondary structure (1); 3D structure after molecular dynamics (MD) simulations (2). (B) Experimental SAXS data fitted by the theoretical SAXS curves calculated from the bead models based on the p(r) (green) and from the MD models (red) of the Gli-233 aptamer (1); an overlap of aptamer’s SAXS-derived structures (green beads) and their 3D models (pink volume) (2). (C) Structures of the Gli-55 aptamer: secondary (1); 3D structure (2). (D) Experimental and theoretical SAXS data of the Gli-55 aptamer. (E) MD simulations of Gli-233-protein interaction at three binding sites to the tubulin dimer (1–3). The ɑ-tubulin chain is gray, and Na+ and ns are shown as blue spheres.