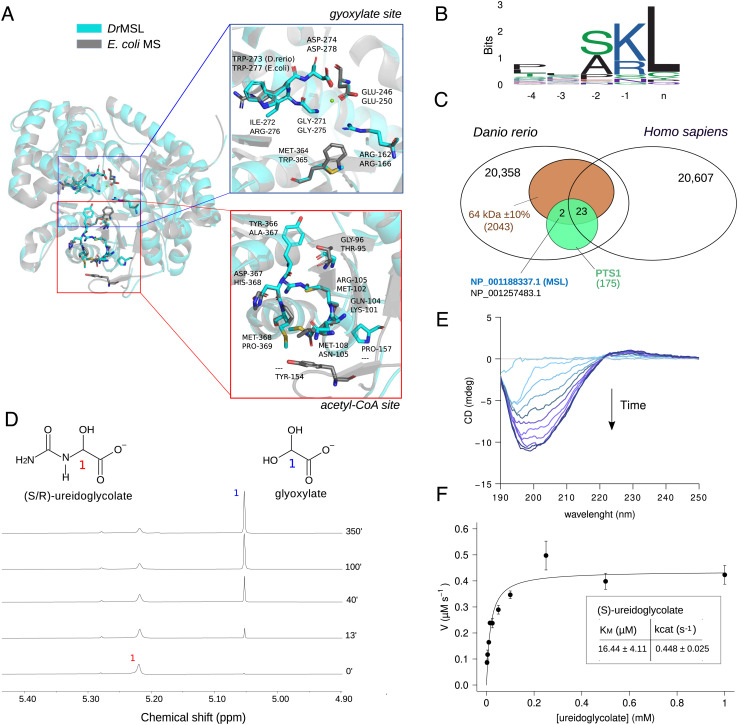
Fig. 5.
Danio rerio malate synthase-like (DrMSL) encodes ureidoglycolate lyase (UGL). (A) Cartoon representation of the DrMSL 3D homology model superimposed on the experimental structure of E.coli malate synthase A (PDB ID: 3CUZ) (41). Residues relevant for MS activity and the corresponding residues in DrMSL are drawn in sticks. The close-up panels show lack of conservation at the acetyl-CoA-binding site (red box) and conservation of residues involved in glyoxylate binding (blue box), except for two substitutions in DrMSL. (B) Sequence logo of MS and MS-like C-terminal sequences of selected eukaryotic species depicting the presence of a PTS1 motif. (C) Venn diagram of Homo sapiens and D. rerio proteomes with intersections defined by the expected features of the UGL enzyme (MW: 64 kDa ± 10%, PTS1 signal, present in D. rerio not in Homo sapiens). Accession numbers of the two proteins retrieved by the search (MSL and “protein brambleberry precursor”) are written in blue and in black. (D) Stacked plots of 1H NMR spectra of 52.5 mM ureidoglycolate in 95% D2O recorded at different time points after the addition of 2 µM DrMSL preincubated with 3 mM MgCl2. (E) Circular dichroism (CD) time-evolution spectra of 2.5 mM ureidoglycolate in the presence of 1 µM DrMSL, showing formation of the (R)-ureidoglycolate spectrum (42). (F) Fitting with the Michaelis–Menten equation of the initial velocity (V0) of 1 µM DrMSL with different substrate concentrations; the calculated kinetics constants are shown in the inset. Error bars represent SD of three independent experiments.