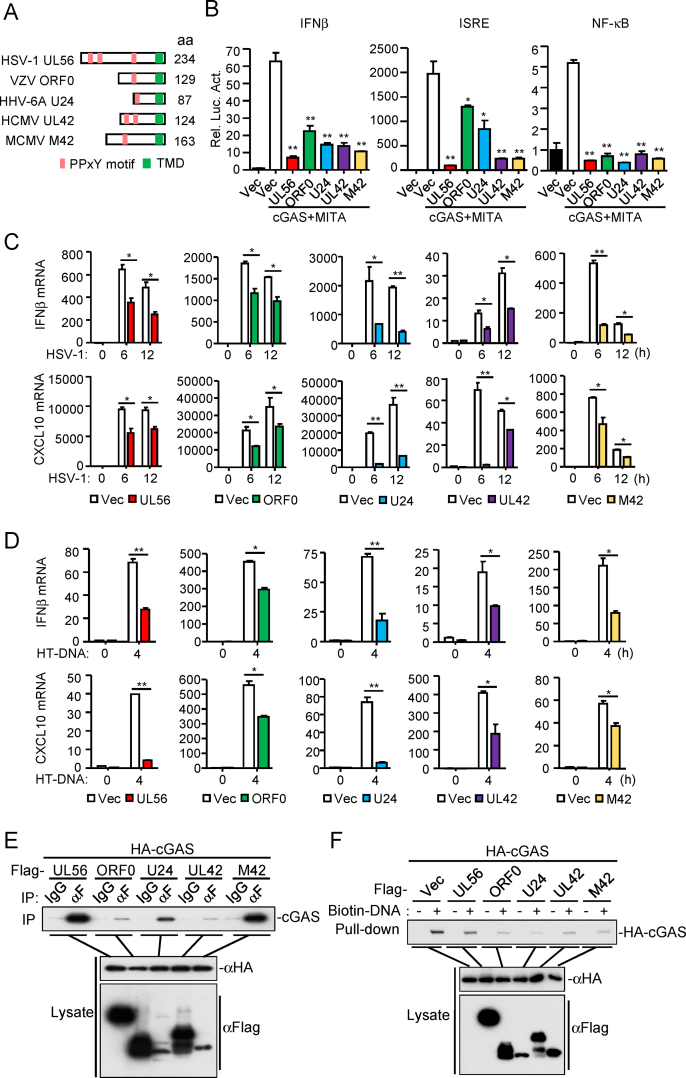
Fig. 6.
Herpesvirus UL56 homologs antagonize cGAS-mediated antiviral responses. (A) Herpesvirus UL56 homologs. PPxY motifs and the transmembrane domain are indicated. (B) UL56 homologs inhibit cGAS-MITA-mediated signaling. HEK293T cells (1×105) were transfected with the IFNβ promoter (50 ng), ISRE (50 ng) or NF-κB (2 ng) reporter plasmids, and expression plasmids for cGAS (10 ng), MITA (15 ng) and the herpesvirus UL56 homolog for 24 h before luciferase assays were performed. (C) UL56 homologs inhibit HSV-1-triggered transcription of antiviral genes. THP-1 cells stably-expressing UL56, ORF0, U24 or UL42 and MLFs stably-expressing M42 were left uninfected or infected with HSV-1 (MOI=1) for the indicated times before qPCR analysis. (D) UL56 homologs inhibit HT-DNA-triggered transcription of antiviral genes. THP-1 cells stably-expressing UL56, ORF0, U24, UL42 and MLFs stably-expressing M42 were transfected with HT-DNA for 4 h before qPCR analysis. (E) Association of UL56 homologs with cGAS. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids for 24 h. Coimmunoprecipitation and immunoblot analysis was performed with the indicated antibodies. (F) UL56 homologs impair the binding of cGAS to dsDNA. HEK293T cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids. Twenty-four hours later, the cell extracts were incubated with biotinylated-HSV120 and streptavidin agarose for 3 h. The bound proteins were analyzed by immunoblots with the indicated antibodies.
The data shown are means ± SD (B–D) from one representative experiment performed in triplicates (3 technical repeats). Similar data were obtained from at least two independent experiments. ∗, p < 0.05; ∗∗, p < 0.01 (Student's unpaired t-test).