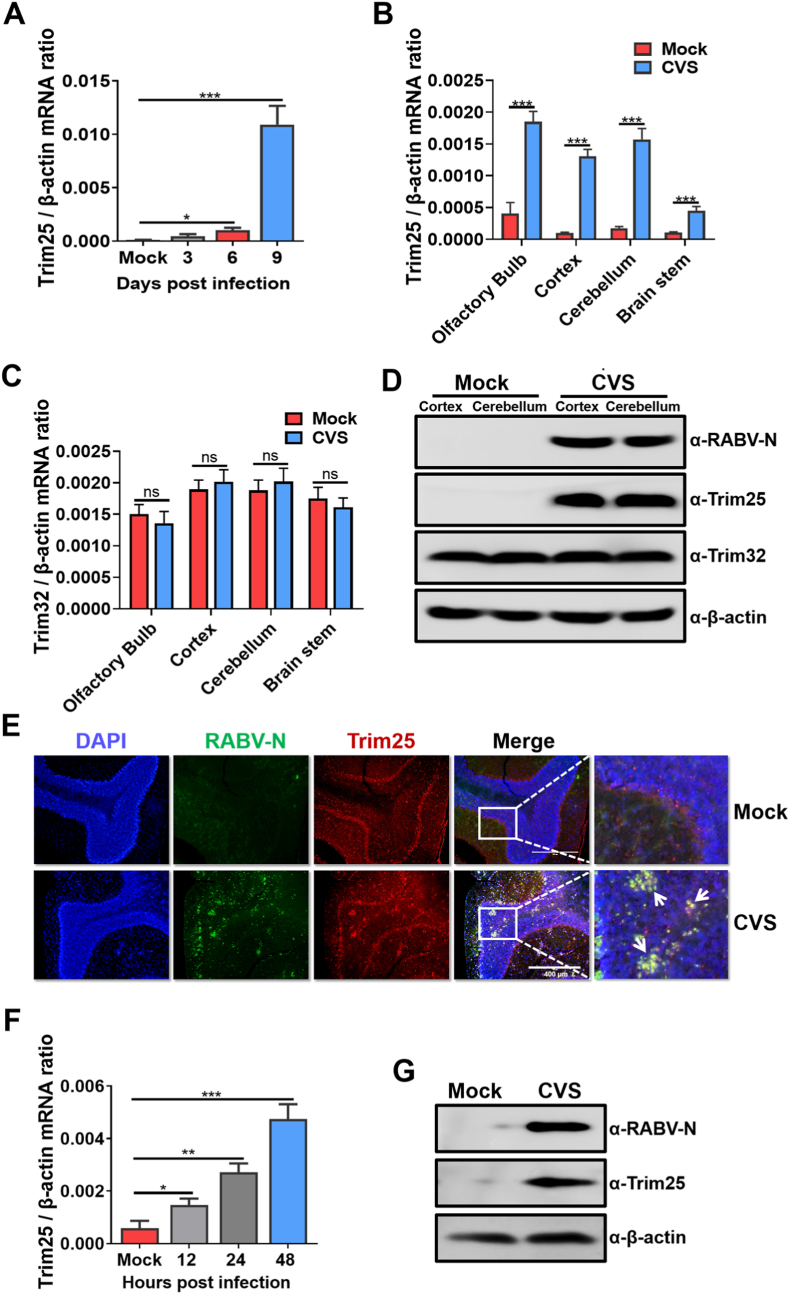
Fig. 1.
Trim25 expression is upregulated after RABV infection. C57BL/6 mice (n = 3) were intracerebrally (i.c.) inoculated with a lab-attenuated RABV strain CVS-B2c (CVS) at 100 FFU or the same volume of DMEM (mock). At 3-, 6-, and 9-days post-infection (d.p.i.), mouse brains were harvested and used for further analysis. (A) Total RNA was isolated from brain tissues, and the mRNA level of Trim25 was analyzed by qPCR. (B) Total RNA from different brain sections (harvested at 9 d.p.i.) was isolated, and the mRNA level of Trim25 was analyzed by qPCR. (C) Total RNA from different brain sections (harvested at 9 d.p.i.) was isolated, and the mRNA level of Trim32 was analyzed by qPCR. (D) The protein levels of Trim25, Trim32, and RABV-N in the cortex and cerebellum of mouse brains harvested at 9 d.p.i. were assessed by Western blotting, and β-actin was used as the control. (E) Mouse cerebellums harvested at 9 d.p.i. were fixed and sectioned. In situ Trim25 expression was analyzed by immunofluorescence assay (IFA). Scale bar, 400 μm. (F) BV2 cells were infected with CVS at an MOI of 1 for the indicated time points, and the Trim25 mRNA levels were measured using qPCR. (G) At 48 h post-RABV infection, BV2 cells were harvested, and the Trim25 protein levels were measured by Western blotting. Error bars represent standard deviation (SD), n = 3. Statistical differences between virus-infected cells and mock infected cells were determined by using Student’s t-test and are denoted as follows: ∗, P < 0.05; ∗∗, P < 0.01; ∗∗∗, P < 0.001. Western blotting data are representative of at least two independent experiments.