Figure 9.
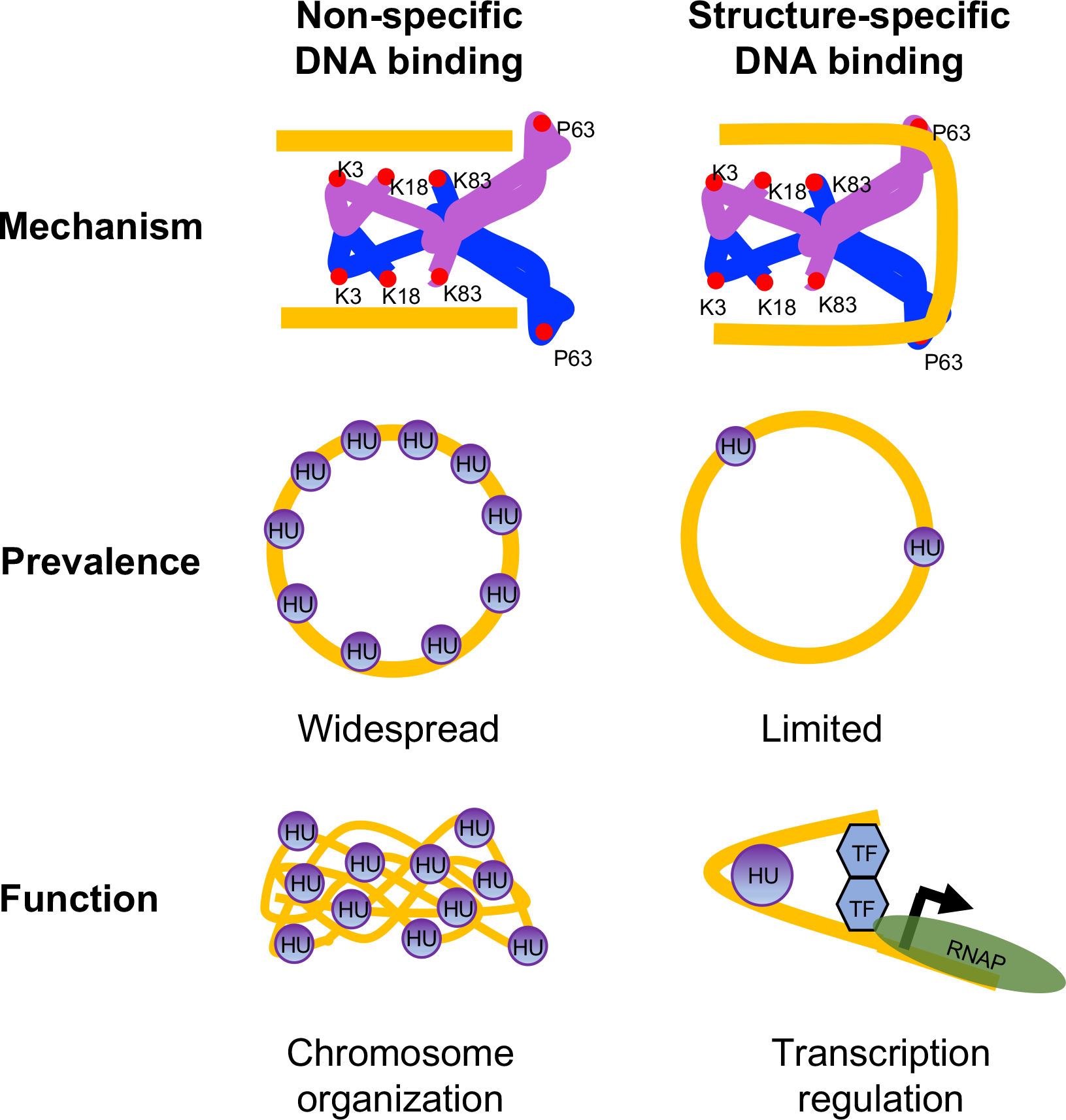
A model for mechanism, prevalence, and function of non-specific and structure-specific DNA binding modes of HU in E. coli
Two subunits of HU are depicted as blue and purple with DNA binding amino acid residues shown as red circles. DNA is depicted in gold. The bound DNA is in the straight conformation in non-specific mode and sharpy bent in structure-specific mode. While non-specific binding mode is widespread in the chromosome and primarily involved in chromosome organization, structure-specific binding mode is limited and involved in transcription regulation. TF Transcription factor; RNAP RNA polymerase.
