Figure 5.
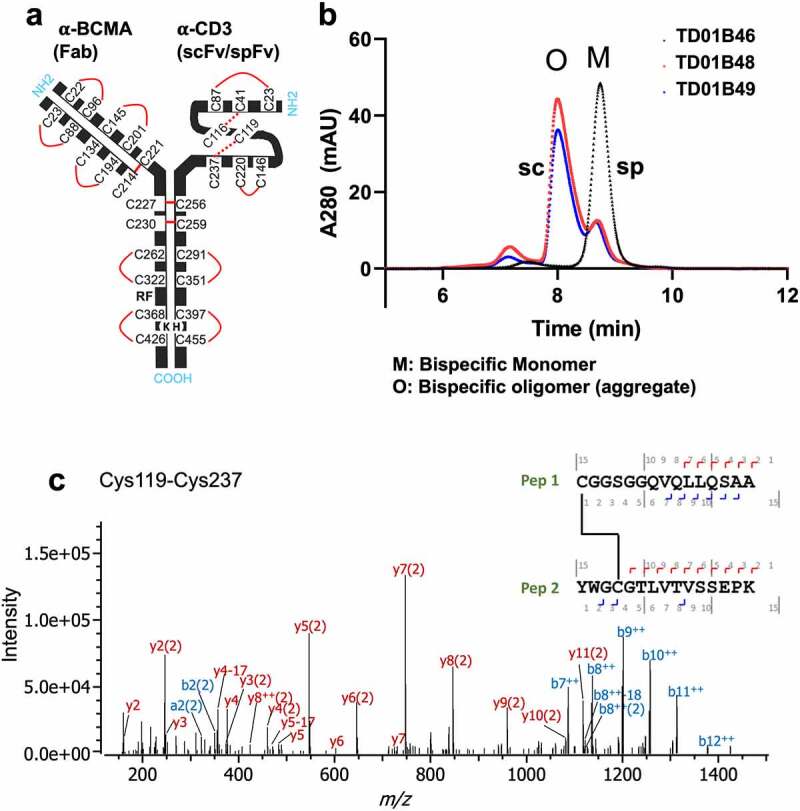
Bispecifics with spFv show improved yields, product quality and expected disulfide formation in the stapled linker. (a) Schematic of BCMA (Fab) x CD3 (scFv/spFv) bispecific molecular architecture. HK in Fc regions indicate the knob-in-hole (K, knob; H, hole) mutations for Fc heterodimerization. RF (H435R and Y436F) mutations in the Fab containing heavy chain are introduced for purification to prevent binding to Protein A of RF containing chain monomers or homodimers. (b) SEC profiles post-CH1 of scFv/spFv Cris7b containing molecules with mAb1 indicate presence of oligomer species (labeled O) in scFv proteins that is absent in spFv proteins (monomer, M). (c) MS2-HCD spectrum of the peptide derived from non-reduced proalanase digestion representing the expected stapled disulfide linkage between Cys119-Cys237. The b- and – y type backbone fragments from each peptide half are annotated in the sequence map that is composed of Pep1 and Pep2 connected via the disulfide bridge.
