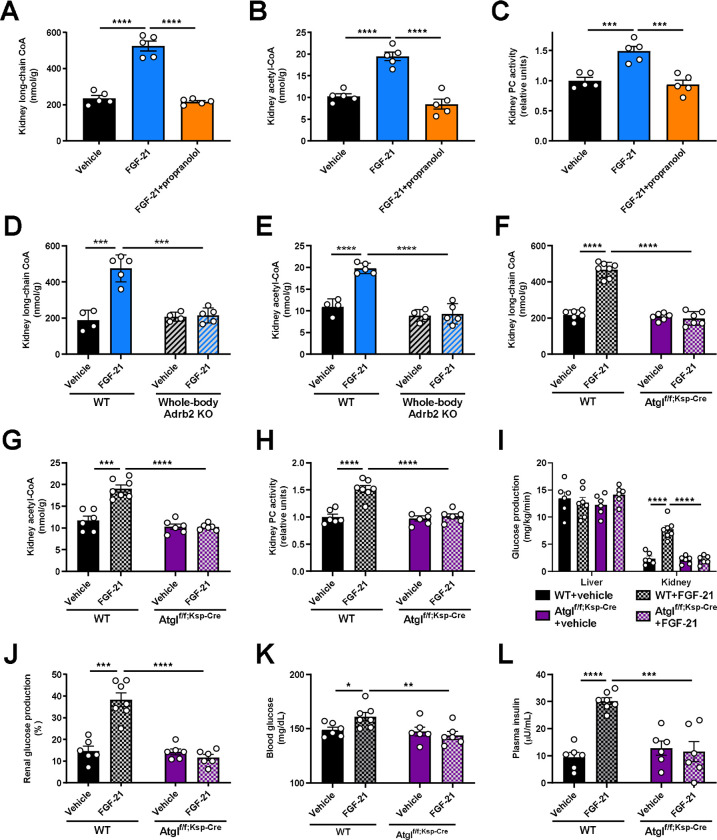
Figure 3. FGF-21-induced increases in renal lipolysis promote increased renal gluconeogenesis in metabolic stress.
(A)-(B) Kidney long-chain acyl- and acetyl-CoA concentrations in mice infused with FGF-21±the nonspecific Adrb antagonist propranolol. In panels (A)-(C), groups were compared by ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, and n=5 per group. (C) Ex vivo pyruvate carboxylase (PC) activity. (D)-(E) Kidney long-chain acyl- and acetyl-CoA concentrations in whole-body Adrb2 knockout mice (n=4 vehicle-treated and 5 FGF-21-treated per genotype). In panels (D)-(L), groups were compared by the 2-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test. (F)-(G) Kidney long-chain acyl- and acetyl-CoA concentrations in kidney-specific ATGL knockout mice (Atglf/f;Ksp-Cre) (n=6 per group with the exception of WT+FGF-21-treated mice [n=7 per group]). (H) Kidney pyruvate carboxylase activity (in panels (H)-(L), n=6 per group with the exception of WT+FGF-21-treated mice [n=7 per group]). (I)-(J) Endogenous glucose production, and the renal contribution to whole-body glucose production. (K)-(L) Blood glucose and plasma insulin concentrations. In all panels, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.