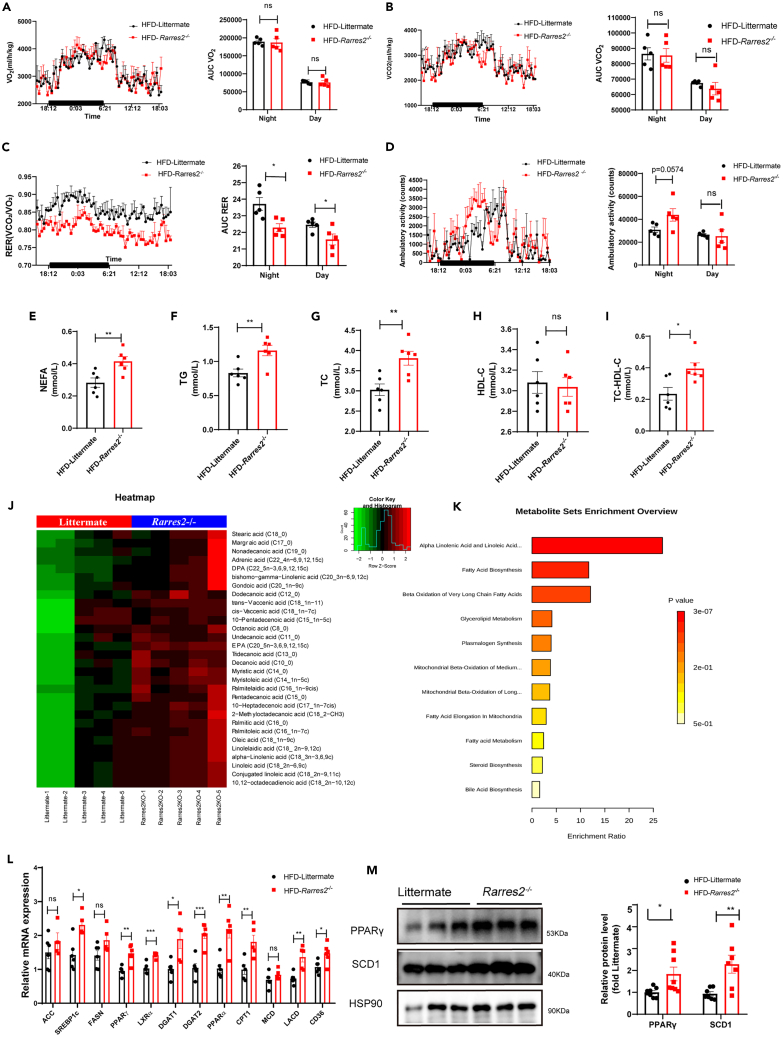
Figure 5.
Chemerin knockout causes metabolic substrate inflexibility and cardiac metabolic dysfunction in HFD mice
Rarres2−/− and Littermate WT mice were subjected to high-fat diet feeding for 20 weeks. Calorimetric parameters about male Rarres2−/− and WT littermate mice were individually placed in the metabolic cages for 2-3 days of measurement; (A) oxygen consumption; (B) carbon dioxide production; (C) Respiratory exchange ratio (RER).
(D) Daily locomotor activity, n = 5. ∗p < 0.05, (E-I) Serum levels of NEFA, TG, TC, HDL-C, and No HDL-C in Rarres2−/− and littermate mice, n = 6.
(J) Metabolic Heatmap and hierarchical clustering of lipid metabolites in the heart of Rarres2−/− and littermate mice.
(K)Top metabolic pathways enriched in Rarres2−/− mice identified by Molecular Pathway Level Analysis (false discovery rate<0.05).
(L) mRNA expression levels of lipogenic genes, n = 6.
(M) Representative Western blots and their quantification of PPARγ and SCD1. The HSP90 was used as a loading control (n = 7). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01.