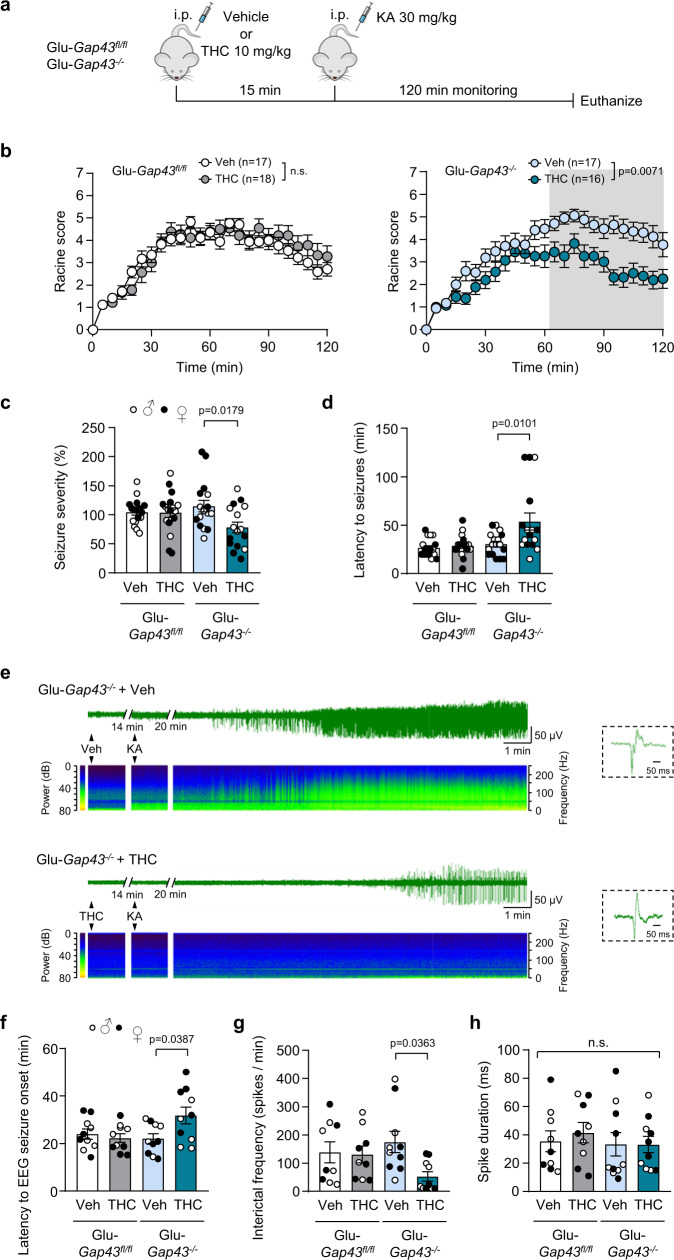
Fig. 6. Enhanced anti-convulsant response to THC in Glu-Gap43−/− mice.
a Timeline of the experiments. Vehicle or THC (10 mg/kg, i.p.; 1 injection) was administered to 3-month-old Glu-Gap43−/− mice and their corresponding Gap43fl/fl littermates. Kainic acid (KA; 30 mg/kg, i.p.; 1 injection) was administered 15 min later, and behavioral score (b–d) or hippocampal EEG recording (e–h) was monitored continuously for 120 min. b Behavioral scoring of seizures using a modified Racine scale (means ± SEM; number of mice in parentheses; the shaded area indicates all the time points at which p < 0.05 by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test;). c Integrated seizure severity, expressed as normalized percentage from Gap43fl/fl/Vehicle group (means ± SEM; Gap43fl/fl/Vehicle n = 17 mice, Gap43fl/fl/THC n = 18 mice, Glu-Gap43−/−/Vehicle n = 17 mice, Glu-Gap43−/−/THC n = 16 mice; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). d Latency to seizures (means ± SEM; Gap43fl/fl/Vehicle n = 17 mice, Gap43fl/fl/THC n = 18 mice, Glu-Gap43−/−/Vehicle n = 17 mice, Glu-Gap43−/−/THC group n = 16 mice; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). e EEG recordings of representative Glu-Gap43−/− mice treated with vehicle (top) or THC (bottom). Epileptic-like spikes appeared after KA injection (insets: detail of individual spikes). The corresponding sonograms (frequency spectrum along recording time) are shown below each recording. f Latency to EEG seizure onset (means ± SEM, n = 10 mice per group; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). g Interictal frequency (means ± SEM; Gap43fl/fl/Vehicle n = 9 mice, Gap43fl/fl/THC n = 9 mice, Glu-Gap43−/−/Vehicle n = 10 mice, Glu-Gap43−/−/THC n = 10 mice; two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). h Average spike duration (means ± SEM; Gap43fl/fl/Vehicle n = 9 mice, Gap43fl/fl/THC n = 9 mice, Glu-Gap43−/−/Vehicle n = 10 mice, Glu-Gap43−/−/THC n = 10 mice; n.s. by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test). Source data are provided as a Source data file.