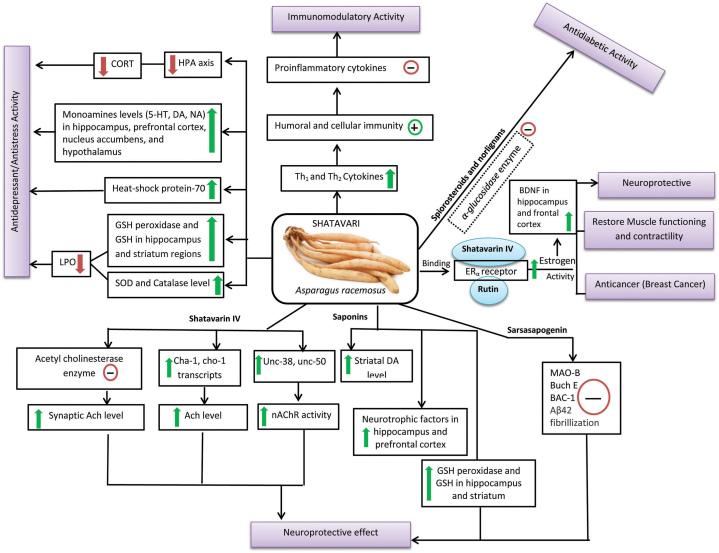
Fig. 4.
Visual representation of therapeutic effects of A. racemosus, the plant possesses multipronged pharmacological properties by modulating various molecular routes. For instance, neuroprotective effects of plant perhaps due to the inhibition of acetyl cholinesterase enzyme, and upregulation of transcripts which subsequently increases the synaptic acetylcholine level and nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR) activity. Alongside, suppression of various enzymes such as MAO-B, Buch E, BAC-1, Aβ42 fibrillation and upregulation of antioxidant enzymes (GSH peroxidase, GSH, Catalase, and SOD) in different brain region promote antidepressant like effects and cerebroprotective properties. Apart from this, the antidepressant effects of Shatavari mediated via modulation of several neurotransmitters and neuronal circuits. Further, downregulation of proinflammatory cytokines improves immune response which delineate immunomodulatory efficacy of the plant. BDNF: Brain derived neurotropic factors; AChE: Acetylcholinesterase; BuChE: Butyrylcholinesterase, 5-HT: Serotonin; DA: Dopamine; NA: Norepinephrine; GSH: Glutathione; GSH peroxidase: Glutathione peroxidase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; CORT: Cortisol; nAChR: Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.