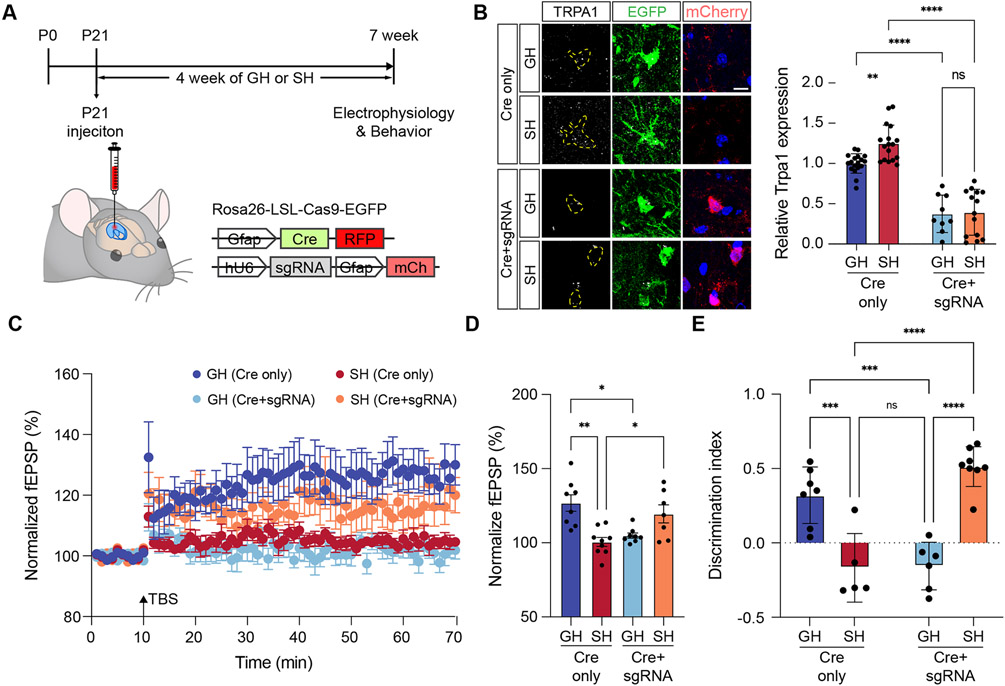
Figure 4. Astrocyte-specific deletion of TRPA1 rescues hippocampal circuit function after social deprivation.
(A) Schematic of Cas9, AAV-based approach for deletion of TRPA1 in hippocampal astrocytes and time line of experimental paradigm.
(B) Immunostaining of TRPA1 in hippocampal astrocytes from control and Cre+gRNA, groups. (n = 9-18 cells from 2 animals in each group) Two-way ANOVA, Tukey tests.
(C-D) Recording of Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) from the hippocampus in GH and SH cohorts treated under control (Cre only) or TRPA1 deletion (Cre+sgRNA) genetic conditions. Two-way ANOVA, Tukey tests.
(E) NPR behavioral studies on GH and SH cohorts under control (Cre only) or TRPA1 deletion (Cre+sgRNA) genetic conditions (n = 5-8 animals in each group). Two-way ANOVA, Tukey tests.
*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.