Fig. 2: Schematics of connections between sensory systems in hearing subjects, simplified.
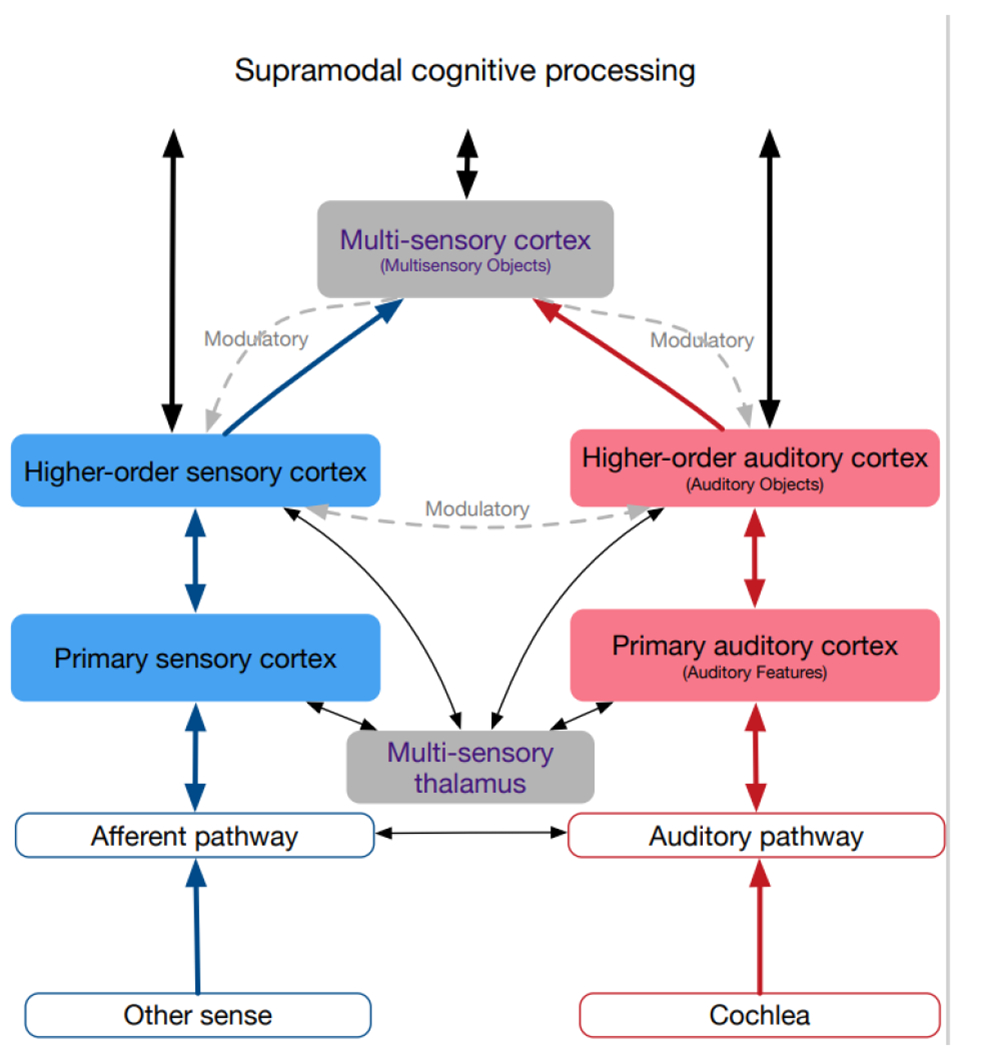
Auditory system shown in red, non-auditory in blue, multisensory in grey. Connections are differentiated into driving (shown as straight lines), defined as connections able to elicit action potentials in absence of other active connections, and modulatory (shown as curved dashed lines), which affect the activity of neurons, but fail to cause postsynaptic action potentials in absence of other inputs (for details, see text). Connections between primary areas not shown since these differ between different sensory cortices. Multisensory information is observable in all cortical areas (filled background), but mainly as a modulatory influence. The main driving input comes from within the sensory system (the adequate input).
