Figure 2.
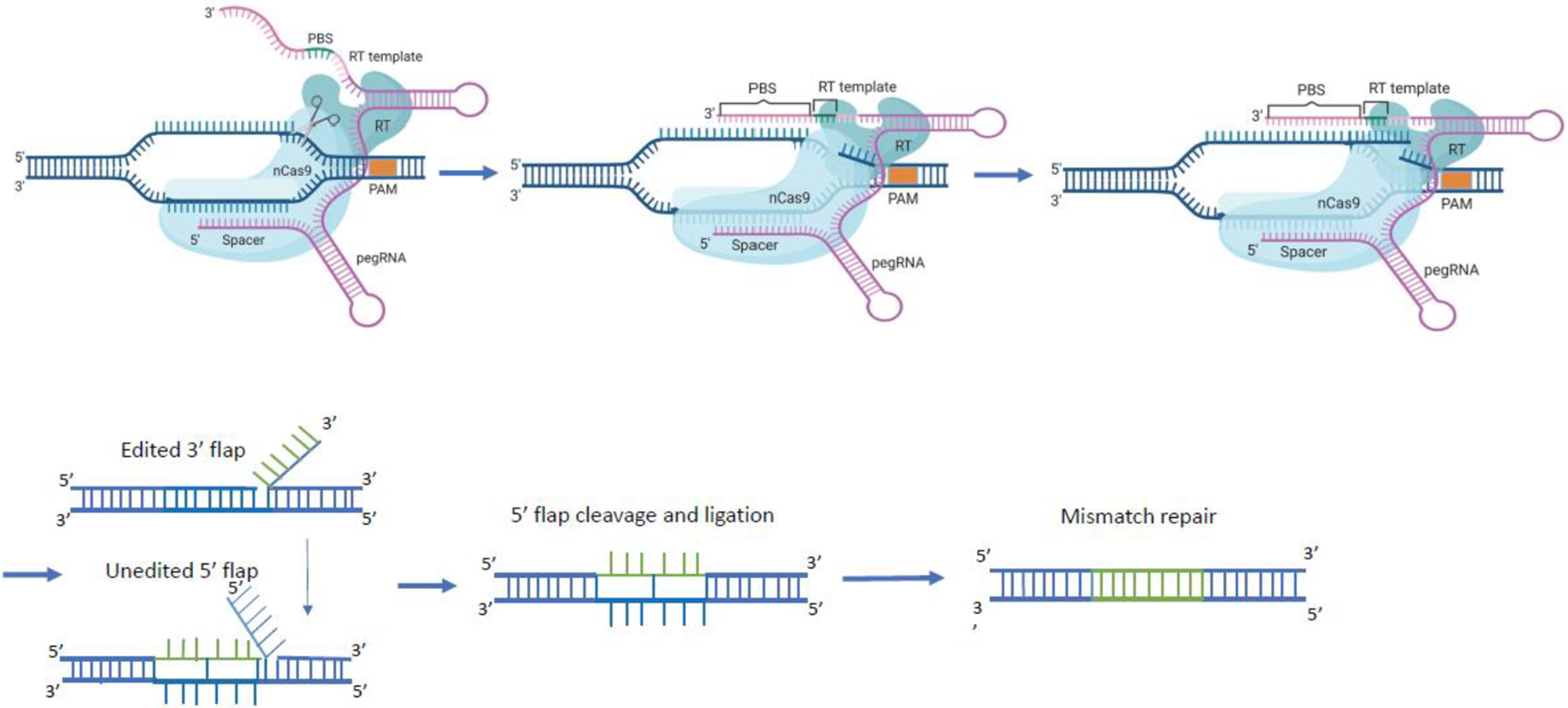
Prime editing components are comprised of a fusion protein of nCas9 (neon blue) with a reverse transcriptase (RT; turquoise) domain and an engineered prime editing single guide RNA (pegRNA; purple). The pegRNA harbors a primer binding site (PBS) and a reverse transcription template (RT) as 3′ extension of the sgRNA scaffold. The pegRNA guides the nCas9 domain to the target site to cut the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM)-containing strand and directs the synthesis of an edited DNA strand starting from the 3′ end of the nicked strand and using the RT sequence (green) as template. The 3′ newly synthesized edited DNA strand can displace the 5′ unmodified DNA strand, resulting in a hybridization of the uncut strand with two DNA flaps. The 3’ flap contains the newly synthesized (edited) sequence and the 5’ flap contains the dispensable, unedited DNA sequence. The 5’ flap is then cleaved by structure-specific endonucleases or 5’ exonucleases. The edited 3’ flap proceeds to ligation and forms a heteroduplex DNA composed of one edited strand and one unedited strand. The reannealed double stranded DNA contains nucleotide mismatches at the location where editing took place. The mismatch repair mechanism is initiated and the information in the edited strand is copied into the complementary strand. Figure created using BioRender.com
