Figure 6. Sublethal endotoxemia induces NFκB subunit p50 binding to consensus sequence in the murine CPR promoter.
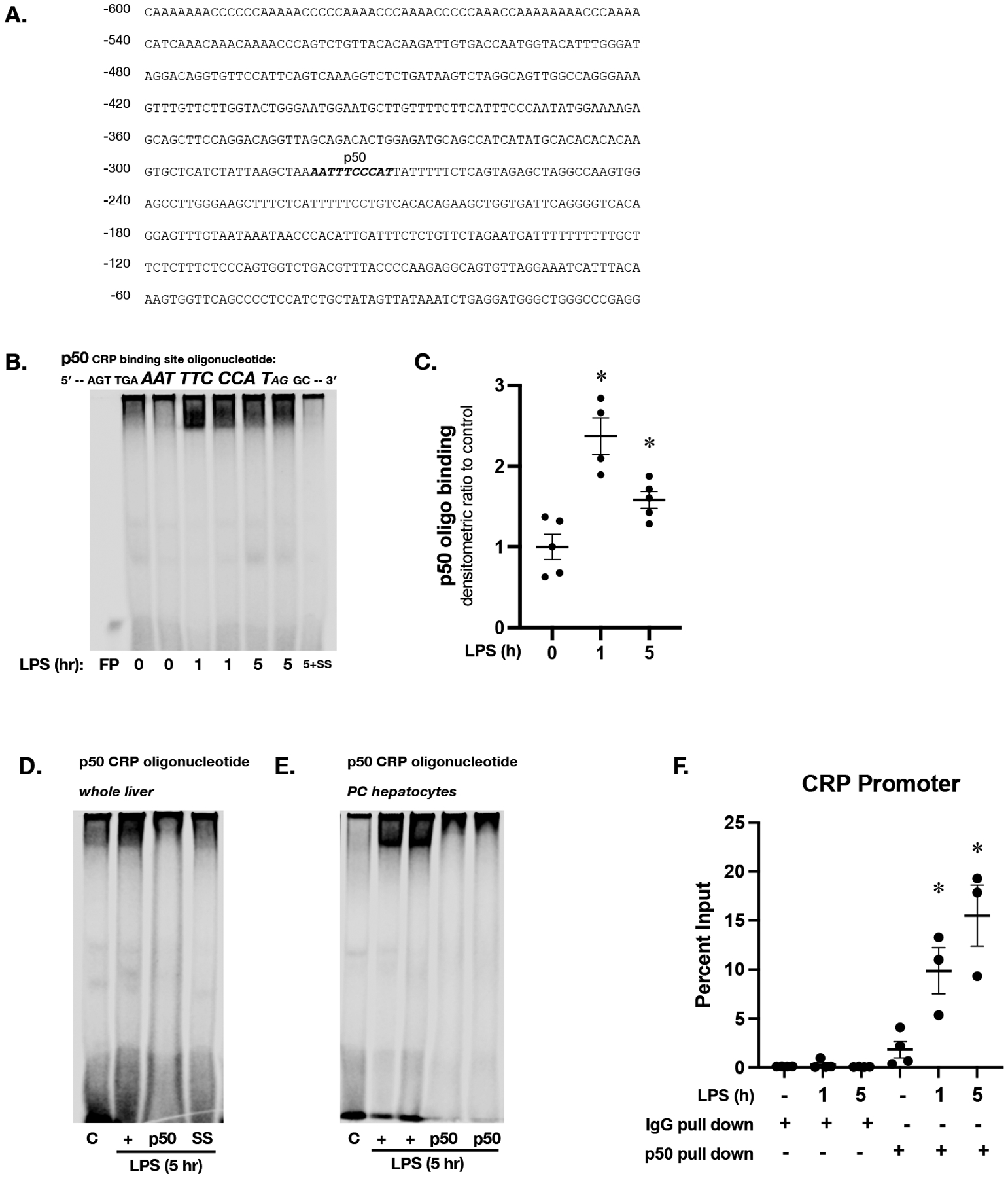
(A) Sequence of the most proximal 600 bases in the promoter of the murine CRP promoter, with putative p50 binding site labeled and in bold italics (B) Representative EMSA using an IR labeled oligonucleotide containing the p50 consensus sequence found in the murine CRP promoter (5’-AGT TGA AAT TTC CCA TAG GC-3’) and hepatic nuclear extracts isolated from mice exposed to endotoxemia (LPS 5 mg/kg, IP; 1 and 5 hours). FP = free probe; SS = salmon sperm (C) Densitometric analysis of p50 consensus sequence binding. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (N = 3 per time point). *p < 0.05 vs. unexposed control. (D) Representative EMSA using an IR labeled oligonucleotide containing the p50 consensus sequence found in the murine CRP promoter (5’-AGT TGA AAT TTC CCA TAG GC-3’) and hepatic nuclear extracts. C = unexposed control; + = LPS exposed (5 mg/kg, IP; 5 hours); p50 = LPS exposed + p50 antibody; SS = salmon sperm. (E) Representative EMSA using an IR labeled oligonucleotide containing the p50 consensus sequence found in the murine CRP promoter (5’-AGT TGA AAT TTC CCA TAG GC-3’) and pericentral hepatocyte nuclear extracts. C = control; + = LPS exposed (5 mg/kg, IP; 5 hours); p50 = LPS exposed (5 mg/kg, IP; 5 hours) + p50 antibody. (F) ChIP qPCR results with primers specific to the p50 binding site of the CRP promoter and hepatic chromatin from endotoxemic (LPS 5 mg/kg, IP; 1 and 5 hours) mice pulled down with either IgG or p50 antibody. Data expressed as mean ± SEM (N = 3 per time point). *p < 0.05 vs. control.
