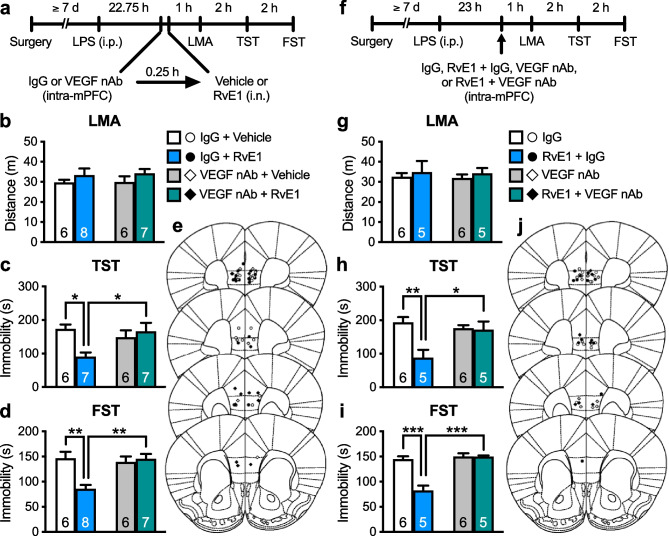
Fig. 3.
Intranasal and intra-mPFC injections of RvE1 produce antidepressant-like actions via VEGF release in the mPFC in LPS-induced depression model mice. a Experimental timeline for LPS challenge (0.8 mg/kg, i.p.), intra-mPFC infusion of either control IgG (80 ng/side) or VEGF nAb (80 ng/side), i.n. administration of either vehicle (0.5% ethanol/PBS) or RvE1 (10 ng/mouse), and behavioral testing. b Effects of intra-mPFC infusion of VEGF nAb and i.n. administration of RvE1 on LMA in LPS-challenged mice (interaction, F1,23 = 0.0125, p = 0.912; VEGF nAb, F1,23 = 0.0571, p = 0.813; RvE1, F1,23 = 2.39, p = 0.136). c, d Effects of intra-mPFC infusion of VEGF nAb on the antidepressant-like actions of i.n. administration of RvE1 in the TST (c, interaction, F1,22 = 6.98, p = 0.0149; one IgG + RvE1-treated mouse was excluded due to tail-climbing) and FST (d, interaction, F1,23 = 11.1, p = 0.0029) in LPS-challenged mice. e Schematic representation of the mPFC infusion sites. Plates are from ref. 36. f Experimental timeline for LPS challenge, intra-mPFC infusion of control IgG (80 ng/side), RvE1 (50 pg/side) + control IgG, VEGF nAb (80 ng/side) or RvE1 + BDNF nAb, and behavioral testing. g–i Effects of intra-mPFC infusion of RvE1 with or without VEGF nAb on LMA (g, interaction, F1,18 = 0.000105, p = 0.992; VEGF nAb, F1,18 = 0.0319, p = 0.860; RvE1, F1,18 = 0.573, p = 0.459) and immobility time in the TST (h, interaction, F1,18 = 7.55, p = 0.0133) and FST (i, interaction, F1,18 = 22.0, p = 0.0002) in LPS-challenged mice. j Schematic representation of the mPFC infusion sites. Plates are from ref. 36. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s post hoc test)