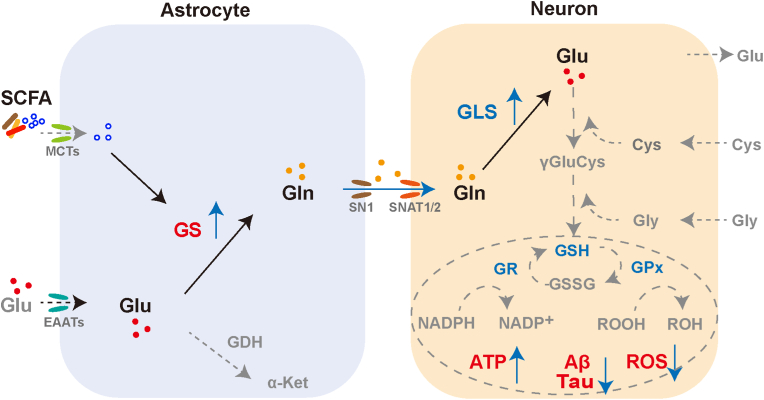
Fig. 7.
Schematic diagram of the model for SCFA-regulated astrocyte-neuron glutamate-glutamine shuttle.
An imbalance between reactive oxygen species production and antioxidant defences is a typical trigger of neuronal damage and death. Astrocytes can efficiently supply neuron with antioxidant substrates to rescue disorders of brain energy metabolism in AD. Astrocytes take up excess glutamate in the synaptic gap, convert it to glutamine via glutamine synthetase and shuttle it to the neurons, where glutamine is reconverted to glutamate by glutaminases. Glutamate in turn is involved in glutathione synthesis and exerts antioxidant effects in neurons. Given that neurons lack the carboxylase for the de novo synthesis of the glutamate, the involvement of astrocytes compensates for the shortcomings of neurons. Our study found that SCFA promote glutamate-glutamine cycle by upregulating astrocyte GS, and consequently countermeasure mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress damage and AD-like lesions. We aim to provide new perspectives on AD prevention and treatment strategies from the regulation of brain energy metabolism (Glu, glutamate; Gln, glutamine; GS, glutamine synthetase; GLS, glutaminase; Cys, cysteine; Gly, glycine; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, glutathione oxidized; GR, glutathione reductase; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; MCTs, monocarboxylate transporters; EAATs, excitatory amino acid transporters; SN1 and SNAT1/2, sodium-coupled neutral amino acid transporters; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; α-Ket, α-Ketoglutarate).