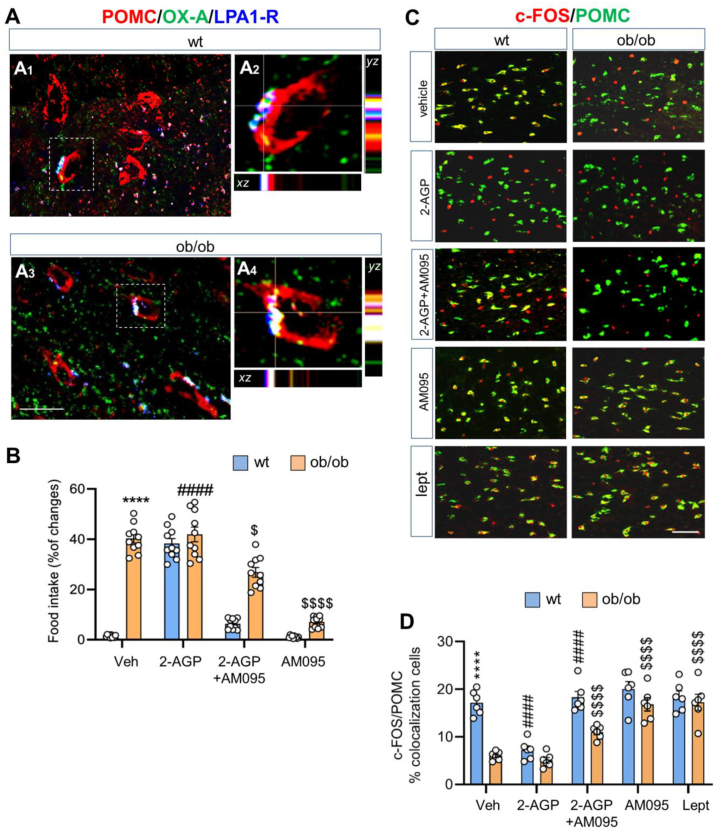
Figure 2.
2-AGP stimulates food intake by modulating POMC neurons. (A) Confocal images of LPA1-R/POMC/OX-A immunolabeling of the ARC nucleus of ad libitum fed) wt (A1–A2) and ob/ob (A3–A4) mice showing LPA1-R immunoexpression at POMC neurons. LPA1-R is expressed diffusely in POMC neurons and in the neuropil of the ARC. (A2, A4). High-power fluorescent micrographs of the resepctive cells inside the boxed area and with orthogonal stacks for wt (A2) and ob/ob (A4) mice; dotted lines and crosshair show 3D coordinates pointing out the LPA1-R/POMC/OXA colocalization. Scale bar: 20 μm (A1, A3) and 10 μm (A1, A3). (B) Effect of 2-AGP on food intake in wt and ob/ob mice. Data are means ± SEM from n = 10 mice/group, two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Each comparison is represented as follows: ∗ = wt vs ob/ob, # = wt vs wt treated, $ = ob/ob vs ob/ob treated mice. (C) Representative images of c-Fos and POMC immunoreactivities in the ARC nucleus of wt and ob/ob mice treated with vehicle, 2-AGP, AM095+2AGP, AM095, and leptin. Scale bar: 100 μm. (D) Bar graph of the quantification of the percentage c-Fos/POMC colocalizing cells. Data are means ± SEM from n = 6 mice/group. The p values were obtained by two-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. Each comparison is represented as follows: ∗ = wt vs ob/ob, # = wt vs wt treated, $ = ob/ob vs ob/ob treated. Overall significance is represented as follow: ∗, #, $p < 0.05, ∗∗∗∗, ####, $$$$p < 0.0001.