Figure 3. Liver cell heterogeneity and reprogramming during NASH.
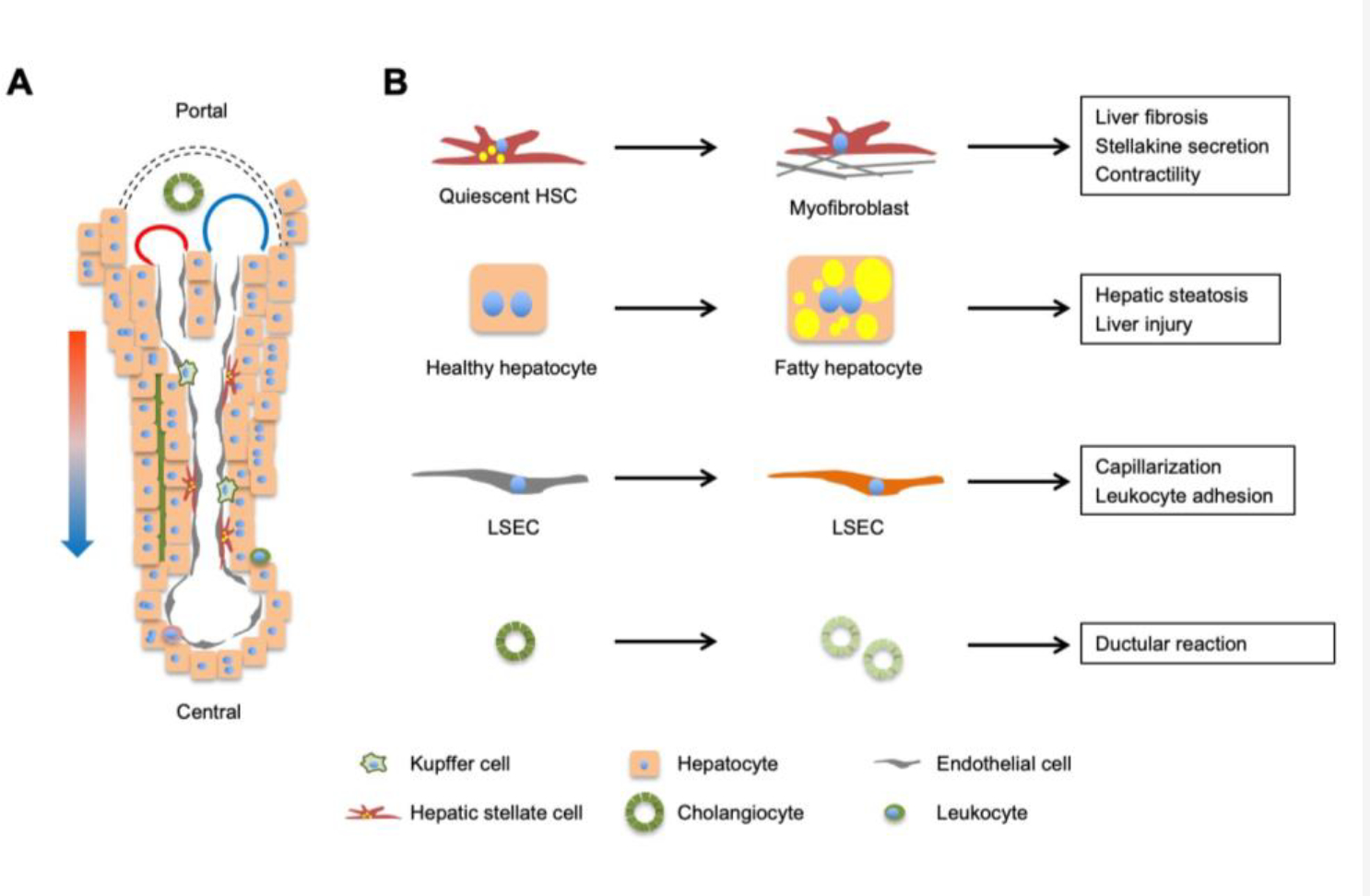
(A) A liver lobule contains parenchymal hepatocytes (60–70% of liver cells) and non-parenchymal cells (30–40%), including sinusoidal endothelial cells, hepatic stellate cells, cholangiocytes, and immune cells (Kupffer cells and leukocytes). Mixed blood from hepatic artery (red) and portal vein (blue) flows along the portal to central direction, creating gradients of oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and gut-derived factors that drive transcriptomic and functional zonation of cells in the liver. (B) Reprogramming of major cell types during NASH pathogenesis. Individual cell types in the liver undergo cell type-specific transcriptomic, metabolic, and functional reprogramming during NASH progression.
