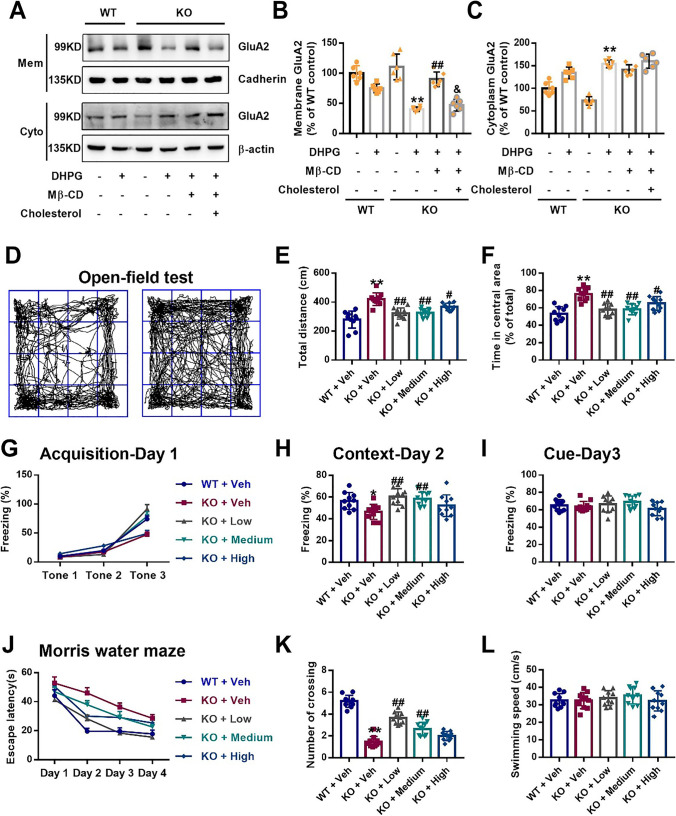
Fig. 7.
Mβ-CD reverses DHPG-induced GluA2 trafficking and abnormal behaviors of adolescent Fmr1 KO mice. A Immunoblots detected GluA2 levels on membranes and in the cytoplasm of hippocampal slices, with pan-cadherin and β-actin as internal control, respectively. B Mβ-CD enhanced the surface level in the KO hippocampus upon DHPG treatment, but the effect was reversed by cholesterol. n = 6 mice per group; ** p < 0.01 versus KO control; ## p < 0.01 versus KO DHPG alone; & p < 0.05 versus KO DHPG and Mβ-CD, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. C The cytoplasmic GluA2 level was slightly decreased under Mβ-CD, although there was no significant difference. n = 6 mice per group; ** p < 0.01 versus KO control, one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test. D Sample traces of locomotor activity in the open field test. E, F Fmr1 KO mice subcutaneously injected with low (125 mg/kg), medium (250 mg/kg), and high (500 mg/kg) doses of Mβ-CD for 2 weeks showed a reduction in the total distance travelled (E) and time spent in center area (F). n = 10 mice per group; ** p < 0.01 versus WT mice; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 versus KO mice. G On training day 1, mice were exposed to three tone-foot shock pairs. KO mice with Mβ-CD exhibited increased freezing during the last phase. H Low and medium doses of Mβ-CD improved contextual fear learning in KO mice. I Mβ-CD had no effect on cued fear learning. n = 10 mice per group; * p < 0.05 versus WT mice; ## p < 0.01 versus KO mice alone. J In the Morris water maze test, KO mice injected with Mβ-CD showed reduced escape latency, with an increase in learning days. K Low and medium doses of Mβ-CD enhanced the number of crossings in KO mice. L No significant difference between groups was observed in swimming speed. n = 10 mice per group; ** p < 0.01 versus WT mice; ## p < 0.01 versus KO mice alone, one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (E–L)