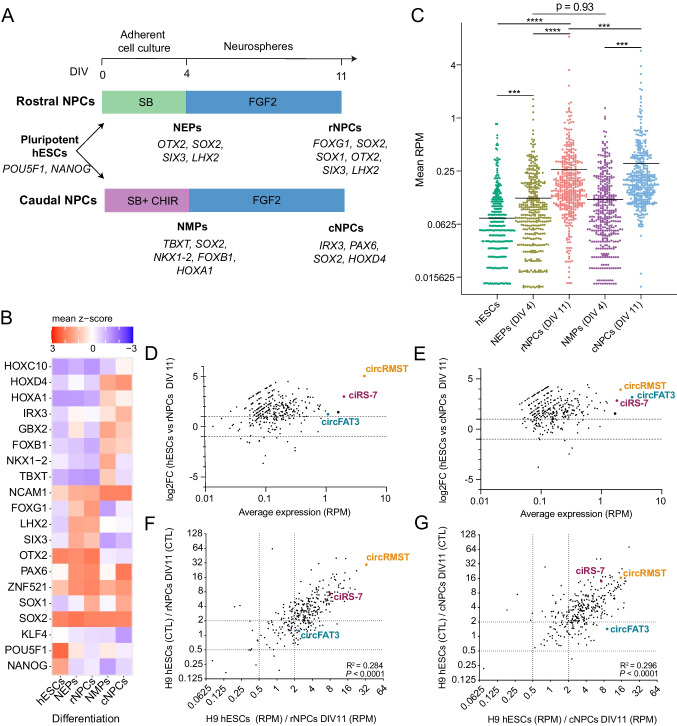
Fig. 1.
Global increase of circRNA expression upon differentiation of human embryonic stem cells into rostral and caudal neural progenitors. A Eleven-day differentiation protocol of H9 human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) into rostral and caudal neural progenitor cells (rNPCs/cNPCs) using SB431542 (SB) and SB plus CHIR99021 (CHIR), respectively, until day four and FGF2 as supplement between day 4 and 11. Differentiations were performed in biological triplicates. B Heatmap showing expression levels of characteristic markers in hESCs, NEPs, rNPCs, NMPs, and cNPCs [35] that were log2-transformed (normalized counts + pseudocount) and converted to a z-scale; n = 3. C Column scatter plot of 417 high-abundance circRNAs detected in hESCs, NEPs, rNPCs, NMPs, and cNPCs; n = 3. Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001. D, E MA plots comparing the 417 high-abundance circRNAs between hESCs and rNPCs (D) as well as hESCs and cNPCs (E). Log2 fold changes, and average expression were plotted; n = 3. F, G Scatter plots of fold changes in RPM and fold changes in circular-to-linear (CTL) ratios of the 417 high-abundance circRNAs for hESCs versus rNPCs (F) and hESCs versus cNPCs (G); n = 3. Correlations were assessed by calculating Pearson’s correlation coefficients, R2, followed by an F-test. RPM, reads per million; DIV, days in vitro