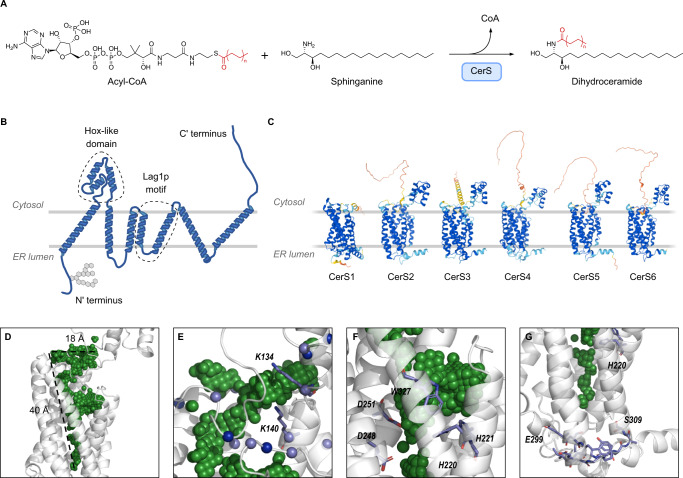
Fig. 1. AlphaFold2 predictions of the structure of the six mammalian CerS.
A Reaction scheme for CerS activity in the ceramide de novo synthesis pathway. B Putative topology of the CerS based on AlphaFold2 predictions. The Hox-like, Lag1p domain, and the N-terminal glycosylation site are indicated. C AlphaFold2 models of human CerS1-6. Note that CerS1 lacks a Hox-like domain. Models are colored by structure prediction confidence as estimated by predicted Local Distance Difference Test (pLDDT) (dark blue, pLDDT >90; light blue, pLDDT of 90–70; yellow, pLDDT of 70–50; orange, <50. D–G CerS5 AlphaFold2 predicted structures showing cavities in the TMD. Protein in gray, cavity volume in green spheres. D The funnel-shaped cavity observed in the CerS5 structure shows a wide opening at the cytoplasmic end of the TMD which narrows towards the ER lumenal end of the TMD. E Positively charged amino acids surround the cytoplasmic end of the TMD in CerS5. Lysine and arginine Cɑ atoms shown as spheres (light blue, lysine; dark blue, arginine). F Putative CerS5 catalytic site showing key residues in stick representation. G The CerS5 specificity loop near the cavity in the TMD. The 11-residue specificity sequence is shown in stick representation with the residues at the beginning (E299) and at the end (S309) indicated.