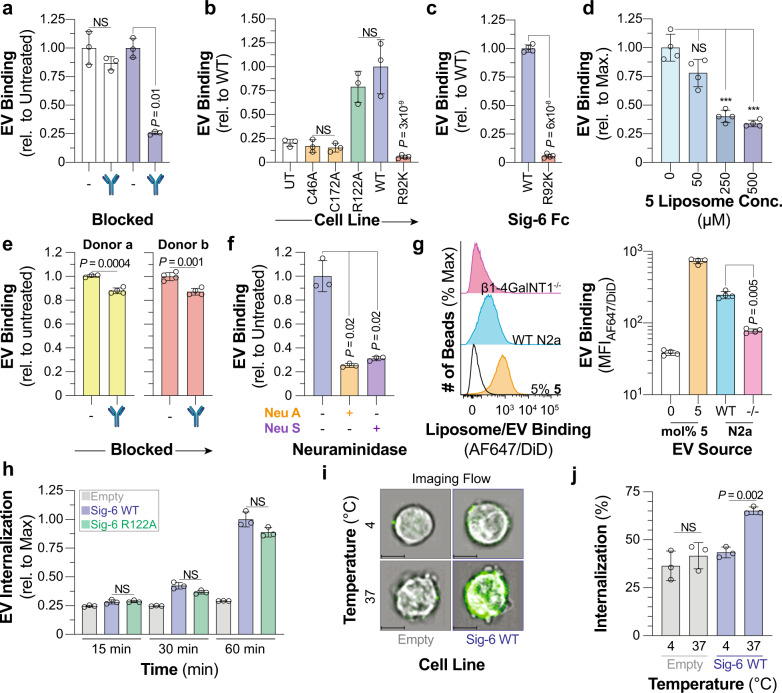
Fig. 6. Siglec-6 binds and internalizes extracellular vesicles through glycolipids independent of its conserved arginine residue.
a Binding of EVs to Siglec-6 expressing CHO cells pre-treated with an anti-Siglec-6 antibody (n = 3 technical replicates). b Binding of EVs to UT CHO cells and CHO cells expressing C46A, C172A, WT, R122A, and R92K Siglec-6 (4 ≥ n ≥ 3 technical replicates). c, Binding of EVs to WT and R92K Siglec-6 in the bead assay (n = 4 technical replicates). d Blocking of EV binding to Siglec-6 with 5 mol% 5 nGLLs in the bead assay (n = 4 technical replicates). e Binding of EVs isolated from two different donors to LAD2 cells pretreated with an anti-Siglec-6 antibody (n = 4 technical replicates). f Binding of neuraminidase A and neuraminidase S treated EVs to Siglec-6 in the bead assay (n = 3 technical replicates). g Binding of EVs isolated from WT and β1-4GalNT1−/− N2a cells to WT Siglec−6 in the bead assay (n = 4 technical replicates). h Time-dependent fluorescence of pHrodo labeled EVs incubated with Daudi cells transduced with WT, R122A Siglec-6, and an empty vector (n = 3 technical replicates). i Representative imaging flow cytometry images of empty vector and WT Siglec-6 virally transduced Daudi cells incubated with AF488 labeled EVs at 4 or 37 °C with the EV fluorescence overlaid over the brightfield image. Scale bars represent 7 µm. j Quantification of internalization of EVs at 4 or 37 °C by Daudi cells transduced with WT Siglec-6 and an empty vector (n = 4 technical replicates). Data is represented by the mean ± one standard deviation of at least three technical replicants. For panel a (WT, C46A, R122A, C172A), b, d, f, g, h, and j a Brown–Forsythe and Welch one-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis. For panels a (WT vs. R92K) c and e a two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for statistical analysis. Not Significant (NS), P > 0.5.