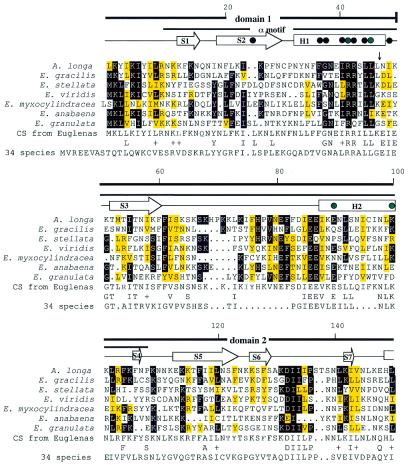
Figure 2.
An rpoA amino acid sequence alignment using PILEUP (GCG Sequence Analysis Package v.8.0). Conserved amino acids in Euglena spp. are indicated by a black background, while similar amino acids are indicated by a yellow background. Similar amino acids are defined as E and D, F and Y, R and K, L, V, I and M, and S and T. Locations of introns are indicated by vertical arrows. The amino acids that were chosen randomly for the Euglena consensus sequence are shown outlined. The consensus of the N-terminal sequence from 34 species of bacteria, algae and land plants is shown. Conserved amino acids between the two consensus sequences are shown and similar amino acids are indicated by a + sign. The secondary structure of the αNTD is indicated schematically above the α sequences; helices H1–H3 are indicated by rectangles; strands S1–S11 are indicated by arrows. Black dots denote residues that participate in the hydrophobic core of the α dimer interface and green dots indicate mutations that cause defects in binding to other subunits that were previously reported for E.coli (14).