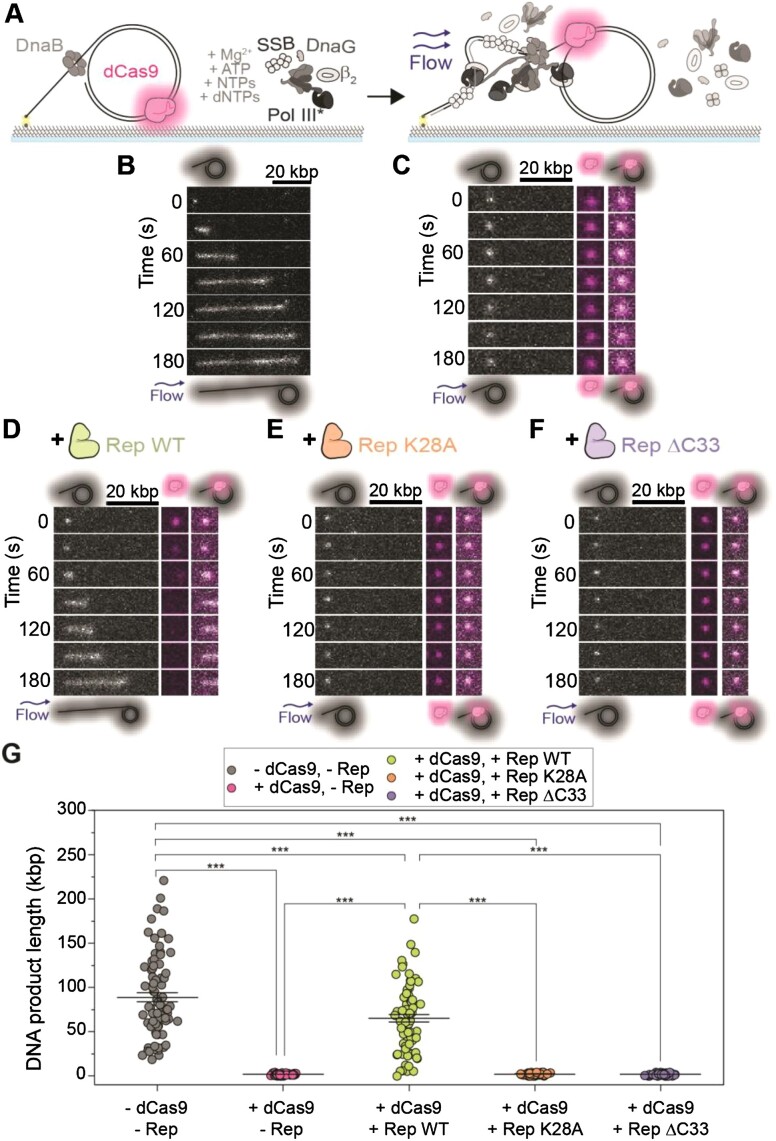
Figure 3.
Visualization of stalled replication rescue by Rep at the single-molecule level. (A) Schematic representation of single-molecule stalled rolling-circle replication assay. The dCas9-cgRNA1-Atto647 complex is pre-incubated with the rolling-circle DNA template, and further incubated with DnaBC before immobilization to the flow cell. The addition of the replisome components results in the initiation of replication until the dCas9-cgRNA1-Atto647 roadblock has been encountered. Stalled replication is imaged by visualizing the Sytox orange-stained DNA (gray) and dCas9-cgRNA1-Atto647 complex (magenta). (B–F) Example montages and (G) mean DNA product length of (B) rolling-circle DNA replication in the absence of protein roadblocks and Rep proteins (89 ± 5 kbp; n= 81; replication efficiency of 4 ± 1% (S.E.M.)). (C) Stalled DNA replication by dCas9-cgRNA1-Atto647 complex in the presence of all replisome components (2.0 ± 0.1 kbp; n= 80; no replicating products observed). (D) stalled replication rescue by Rep WT following removal of the dCas9-cgRNA1-Atto647 complex (65 ± 4 kbp; n= 75; 2 ± 1%). (E) Stalled replication in the presence of Rep K28A (2 ± 1 kbp; n= 80; no replicating products observed). (F) stalled replication in the presence of Rep ΔC33 (2 ± 1 kbp; n= 80; no replicating products observed). (G) Total DNA product length after 3 min, where bars represent the reported mean ± S.E.M, as listed for (B–F). Comparison of distributions was conducted using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons post-hoc test, where *** denotes statistical significance with p ≤ 0.001 and absence of markers indicates no significant difference (p > 0.05).