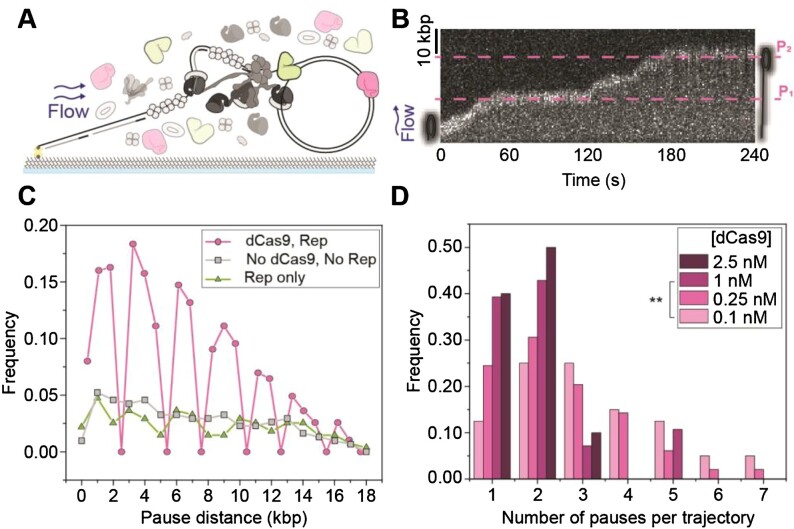
Figure 4.
Observations of multiple stalling events. (A) Schematic representation of single-molecule stalled replication rescue assays, pre-incubated with DnaBC and immobilized to the flow cell surface. Replication is initiated in the presence of Rep and dCas9-cgRNA1. (B) Example 18-kbp rolling-circle DNA template undergoing multiple replication stalling and rescue events, at approximately 17 kbp (P1) and 36 kbp (P2). The target site of the dCas9-cgRNA1 complex occurs once every 18 kbp of the DNA template. (C) Pairwise distance analysis of the pause site replication rescue events on the 2-kbp DNA template in the presence of 10 nM Rep-AF647 and 0.25 nM dCas9-cgRNA1 (magenta, 16 pauses/275 kbp), only Rep-AF647 (green, 16 pauses/275 kbp) and absence of both proteins (gray, 18 pauses/307 kbp), for the first 20 kbp of DNA products. Symbols represent the distribution of histogram bin heights, normalized to the total DNA product length. Pauses in the absence of dCas9-cgRNA1 represent spontaneous pausing of the replisome. (D) Histograms of the number of pauses per replicating molecule at titrated dCas9-cgRNA1 complexes in the presence of 10 nM Rep-AF647 using the 2-kbp rolling-circle DNA template; 2.5 nM dCas9-cgRNA1, 17 pauses from 10 molecules (mean of 2 ± 1 (S.D.), replication efficiency of 1 ± 1% (mean ± S.E.M.); 1 nM dCas9-cgRNA1, 56 pauses from 30 molecules (2 ± 1; 1 ± 1%); 0.25 nM dCas9-cgRNA1, 128 pauses from 51 molecules (3 ± 2; 3 ± 1%); and 0.1 nM dCas9-cgRNA1, 130 pauses from 43 molecules (3 ± 2; 3 ± 1%). Comparison of the mean number of pauses per trajectory was conducted using one-way ANOVA with Tukey's comparison post-hoc test, where ** denotes statistical significance with p ≤ 0.01 and absence of markers indicates no significance difference (p > 0.05).