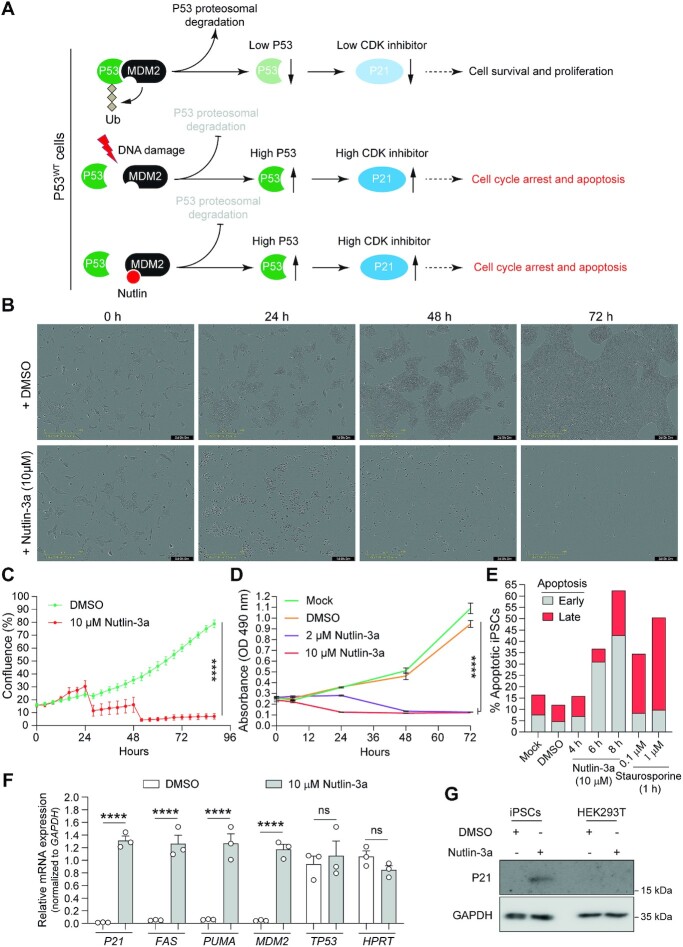
Figure 7.
Cell survival assay for assessing P53 functionality in human iPSCs. (A) Schematics of post-transcriptional P53 activity control by DNA damage and Nutlins. In cells with normal amounts of P53, DNA damage activates ATM/ATR kinases that disrupt P53-MDM2 interaction through P53 phosphorylation. Free P53 escapes proteasomal degradation and upregulates the expression of downstream target genes (e.g. cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor P21) inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Nutlins disrupt the P53-MDM2 interaction by instead occupying the P53 binding pocket in MDM2 mimicking a P53-dependent DNA damage response. Conversely, in cells with no or low amounts of P53, nutlins induce neither cell cycle arrest nor apoptosis (not drawn). (B and C) Realtime cell proliferation assay. The proliferation of human iPSCs incubated in the presence of Nutlin-3a (10 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) was quantified in a live-cell imaging system (IncuCyte) for 3 days. Data are shown as mean ± SD of 6 technical replicates. Significant differences between the indicated datasets were calculated by two-way ANOVA tests; ****P < 0.0001. (D and E) Cell survival assays. The survival of human iPSCs incubated in regular medium (Mock) or in medium supplemented with DMSO or Nutlin-3a (2 μM and 10 μM) was monitor for 3 days by using the MTS cell metabolic activity readout (panel D). The frequencies of apoptotic human iPSCs were determined with a combined annexin V/propidium iodide assay (panel E). Annexin V positive cells and annexin V/propidium iodine doubly positive cells measured by flow cytometry scored for early and late apoptosis, respectively. Prior to flow cytometry the cells were incubated in regular medium (Mock) and in medium supplemented with DMSO or with Nutlin-3a (10 μM) for different periods. Staurosporine applied at the indicated conditions served as an apoptosis-inducing control. (F) Assessing P53-dependent responses in human iPSCs exposed to Nutlin-3a. RT-qPCR analysis of transcripts for P53 and P53-responsive genes were conducted in human iPSCs incubated for 5 h in regular medium or in medium supplemented with Nutlin-3a (10 μM). RT-qPCR analysis of HPRT1 transcripts served to measure the expression of a P53-independent control gene (n = 3 independent biological replicates). Significances were calculated with two-way ANOVA followed by Šidák's test for multiple comparisons; ****P < 0.0001; P> 0.05 was considered non-significant (ns). (G) P53-dependent P21 protein detection assay. Western blot analysis of P21 expression in human iPSCs incubated in the presence of Nutlin-3a (10 μM) or vehicle (DMSO) for 12 h. Transformed P53-defective HEK293T cells exposed to the same experimental conditions served as control. Western blotting of the housekeeping GAPDH provided for loading controls.