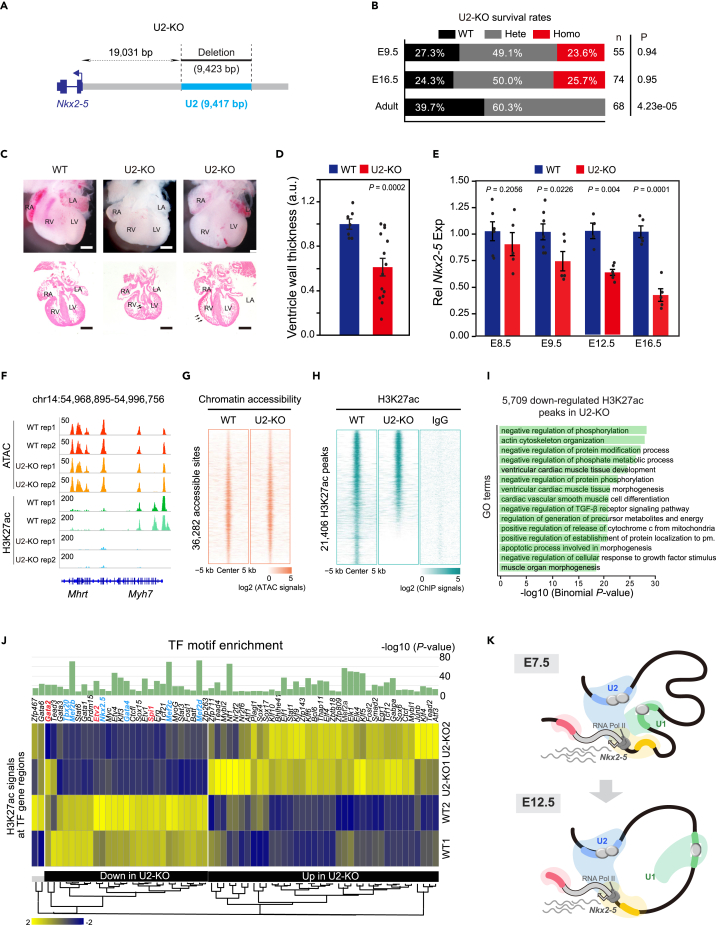
Figure 6.
Characterization of U2-KO heart malformation and chromatin states
(A) Schematic of the strategy for the U2-knockout (U2-KO) mice generation.
(B) Survival analysis of U2-KO strains determined by heterozygote intercrosses at three indicated developmental stages. p-value was calculated by chi-squared test.
(C) Gross heart morphology and H&E staining of sections of E16.5 U2-KO and WT hearts. Arrows indicate ventricular septal defect (VSD) and thinner ventricle wall. Scale bar, 500 μm.
(D) Quantification analysis of the right ventricle thickness in (C). Data were mean ± s.e.m. p-value was calculated by Student’s t-test.
(E) RT-qPCR of Nkx2-5 in WT and U2-KO embryonic hearts at E8.5, E9.5, E12.5, and E16.5. Data were mean ± s.e.m. p-value was calculated by Student’s t-test.
(F) Track view showing ATAC-seq and H3K27ac ChIP-seq signals at Nkx2-5 or Myh7 locus in E16.5 heart apex.
(G) Heatmaps showing ATAC-seq signals at non-duplicated 36,282 peaks from all replicates. Each column was plotted at the 10 kb regions of the peak centers, and rows were sorted by log2 (WT+1)/log2(U2-KO+1) ATAC-seq signals.
(H) Heatmaps showing H3K27ac ChIP-seq signals at non-duplicated peaks from all replicates. Each column was plotted at the 10 kb regions of the peak centers, and rows were sorted by log2 (WT+1)/log2(U2 -KO+1) signals. log2 (ChIP signals) were shown in 15,501 peaks with WT/U2-KO > 1 and 5,095 peaks with WT/U2-KO ≤ 1.
(I) Bar plot showing top 15 GO terms enriched in genes nearby 5,709 significantly (FDR ≤ 0.05) downregulated H3K27ac peaks in U2-KO hearts. p-value was calculated by the Binomial test.
(J) H3K27ac ChIP-seq signals at TF regions whose motifs were enriched in down/upregulated H3K27ac peaks in E16.5 U2-KO hearts. TF motif p-value was calculated by Binomial test, and the H3K27ac signals were scaled by row Z score. Several cardiac feature genes were highlighted by blue, and the hematopoietic feature genes were highlighted by red.
(K) A working model showing the regulatory mechanisms of U1 and U2 regulating Nkx2-5 transcription during heart development. As early as E7.5, U1 and U2 work additively to sustain Nkx2-5 transcription, both of which could compensate for the loss of each other. From E12.5 and onward, U1 becomes insufficient to support Nkx2-5 expression. See also Figures S6 and S7.