Fig. 1.
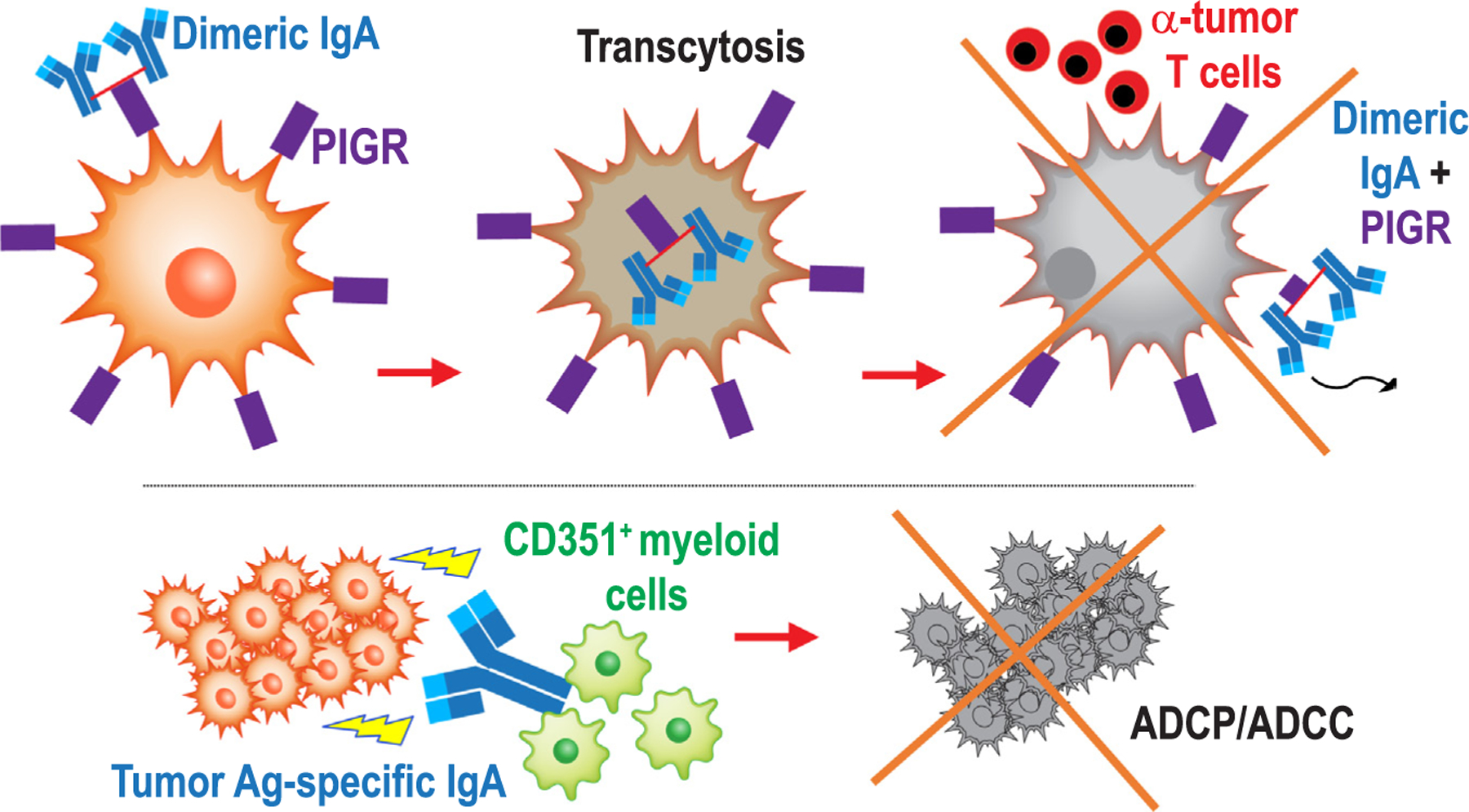
Antigen-dependent and independent mechanisms of anti-tumor activity elicited by IgA at tumor beds. IgA dominates the antibody response in ovarian and endometrial cancer, driving anti-tumor immunity through a dual mechanism: On one hand (top), dimeric IgA transcytoses through tumor cells, which quasi-universally express the IgA/IgM receptor PIGR, which sensitizes tumor cells to T cell-mediated killing. On the other hand, IgA targeting multiple tumor cell transmembrane molecules re-directs myeloid cells against malignant cells, resulting in ADCP-mediated killing.
